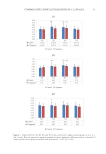
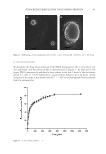
21 TESTING OF HAND CREAMS Minimum inhibitory concentration (30) was determined by inoculating two batches of the same bacterial suspension with the three test strains at 1 × 106 CFU mL−1. The four bacteriostatic components were added to the first batch of bacterial suspensions at 10, 15, 25, 50, 75, 100 μL mL−1, and the second batch was used as the blank control solution. The two batches of bacterial suspensions were incubated at 37 ± 1°C for 24 h in a constant temperature incubator, at which point the absorbance was measured. The minimum inhibitory concentration was designated as when the change in absorbance (OD) of the two corresponding batches reached ≤0.05. To determine the size of the inhibition zone (31), a sterile cotton swab was dipped into the test bacteria suspension with a concentration of 5 × 105 to 106 cfu mL−1 and smeared evenly on the surface of a nutrient agar medium plate. Using sterile tweezers, a sample piece was placed on the surface of the plate. The petri dish was incubated at 37°C for 16 to 18 h before observing the results. The diameter of the antibacterial ring (including the patch) was measured with a vernier caliper and recorded. This test was repeated three times and the average value was taken. If the diameter of the inhibition ring was greater than 7 mm, the test agent was considered bacteriostatic. To test the bacteriostatic rate (31), the sample was added in an Erlenmeyer flask to 70 mL of phosphate buffer (0.03 mol L−1, pH value 7.2–7.4) and 5 mL of bacterial suspension (1–5 × 104 cfu mL−1). The solution was sampled (1 mL) before shaking at 300 r min−1 for 2 min Table III Bacterial Strains Serial number Strain name Code Source 1 S aureus ATCC 6538, fifth generation Guangdong microbial strain collection center 2 C albicans ATCC 10231, fifth generation Guangdong microbial strain collection center 3 E coli ATCC 8099, fifth generation Guangdong microbial strain collection center Table II Raw Materials for Bacterial Test Serial number Raw material name Specification (w, %) Source Remarks 1 Tryptone 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Biochemical grade 2 Peptone 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Biochemical grade 3 Glucose 99 Shandong Yiwei’an Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. Analytical Reagent 4 Sodium chloride 99.5 Shandong Yiwei’an Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. Analytical Reagent 5 Agar 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Food grade 6 Soy peptone 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Biochemical grade 7 Tween 80 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Food grade 8 Lecithin 99 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Food grade 9 Sodium thiosulfate 98 Henan Kangzhiwang Biological Technology Co., Ltd. Food grade
22 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE at 20 to 25°C. Thereafter, 1.0 mL was diluted with a phosphate buffer to 10−2. The liquid was sampled after shaking and then returned to shaking for different times under the same temperature and speed conditions. The sample solutions from before and after the shaking were inoculated onto the plate using the agar pouring method, and the viable bacteria were counted. Each sample was tested three times according to the following formula and the average values were obtained for comparison: Bacteriostatic rate Average difference between colony count = before and after the test Average number of colonies befo the test ×100% A hand cream disinfection field trial (31) was conducted by washing the test area of the subject’s hand with liquid soap and then inoculating three test microorganisms. The sample product (1 g) was taken and applied to the test area. After 3 min of action, the infected area was covered with a metal tube, 1.0 mL of neutralizing agent was aspirated and transferred to the metal tube, which was then scraped with a nylon spatula for 60 s. This whole process was repeated twice. The scraping liquid was aspirated to the test tube as a sample for the test group. On the other hand, the same treatment was done with distilled water instead of product as the control group sample, and the number of recovered colonies was 2 × 106−107 cfu, and the test was valid. Finally, the killing log value was calculated. Table IV Instrumentation Used in the Experiments Serial number Name Model Manufacturer 1 Electric heating vacuum constant temperature drying oven DZF-1B Shanghai Yuejin Medical Instruments Co., Ltd. 2 Laboratory continuous high-shear emulsifying machine SG500 Shanghai Shanggui Fluid Instruments Co., Ltd. 3 Constant temperature magnetic stirrer C-MAG HS 7 IKA Works Guangzhou 4 Electronic analytical balance HZK-FA110 Huazhi Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd. 5 Desktop high-speed centrifuge TG16-WS Hunan Xiangyi Laboratory Instrument Development Co., Ltd. 6 Precision motorized stirrer JJ-1 Jiangsu Kexi Instrument Co., Ltd. 7 Digital rotational viscometer NDJ-5T Shanghai Fangrui Instrument Co., Ltd. 8 pH meter PB-10 Sartorius Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd. 9 Constant temperature culture oscillator ZWY-240 Shanghai Zhicheng Analytical Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. 10 Stainless steel vertical sterilizer YXQ-LS-70A Hebei Huicai Technology Co., Ltd. 11 Alarm intelligent safety ultra-clean workbench ZHJH-C1112C Shanghai Zhicheng Analytical Instrument Manufacturing Co., Ltd. 12 Refrigerator BCD-460WGHF D14NZU1 Haier Group 13 UV spectrophotometer N2 Shanghai Precision Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd. 14 Skin testing instruments MPA580 Courage + Khazaka Electronic, Germany
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)