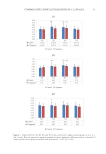
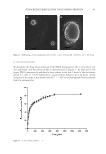
31 TESTING OF HAND CREAMS after 1 and 2 weeks, respectively. Even considering the differences in the volunteers’ skin types, their transdermal water loss was reduced by an average of 14.7% after using the hand cream for 1 week, and an average of 28.4% after 2 weeks of use. CONCLUSION Using compound plant extracts, we developed a purple antibacterial hand cream. According to the inhibition zone, the C reticulata peel extract and L erythrorhizon extract combined at a 2:1 ratio exerted a potent bacteriostatic effect. The average inhibitory rates against S aureus, C albicans, and E coli after 2 min were 92.46%, 92.33%, and 97.61%, respectively. A field test established that this cream has potent antibacterial and disinfecting effects. Through viscosity, pH, centrifugation, and thermal stability tests, the hand cream created in the present study proved itself stable in quality. Its outstanding moisturizing and skin care effects were confirmed by sensory and skin care efficacy evaluations by a study group. Based on these findings, this hand cream can satisfy people’s daily moisturization needs while also slowing the spread of microorganisms. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the 2021 Zhongyuan Academician (Famous Teachers) Foundation of China (GDXX2020DYP010). REFERENCES (1) P. J. Pawlica, The influence of cosmetics on the bacterial flora of the skin, EJMT, 24(3), 44–52 (2019). (2) B.Y. Qiu, Modern Cosmetics Science and Technology. (China Light Industry Press, Beijing, 2016), pp. 1331–1387. (3) W.P. Zhang, Skin care emulsion and cream (end), Science of Daily Chemicals, 42, 54–58 (2019). (4) K. Sakamoto, Cosmetic science and technology: theoretical principles and applications (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2017). (5) H.A.E. Benson, M.S. Roberts, and V.R. Leitesilva, Cosmetic Formulation: Principles and Practice (CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 2019), pp. 1–28. (6) G.M.D.A. Costa, G.A.D. Alves, and P.M.B.G.M. Campos, Application of design of experiments in the development of cosmetic formulation based on natural ingredients, International Journal of Phytocosmetics and Natural Ingredients, 6(1), 4 (2019). Table XIII Skin Moisture Content and Percutaneous Moisture Loss Changes Volunteer Skin moisture content change (%) Transdermal water loss change (%) After 1 wk After 2 wk After 1 wk After 2 wk A +18.0 +29.8 −10.2 −31.5 B +19.7 +29.9 −11.6 −30.8 C +8.7 +28.4 −16.0 −23.6 D +16.5 +28.8 −21.1 −27.7 Average change (%) +15.7 +29.2 −14.7 −28.4
32 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE (7) S. Alam, M.S. Algahtani, and M.Z. Ahmad, Investigation utilizing the HLB concept for the development of moisturizing cream and lotion: in-vitro characterization and stability evaluation, Cosmetics, 2(7), 43 (2020). (8) F.H. Hu, Selection of cosmetic raw materials, Daily Chemical Science, 32(8), 45–47 (2009). (9) M.L. Liu and H.J. Niu, Selection of cosmetic raw materials, Jiangxi Chemical Industry, 31(3), 123–124 (2015). (10) Y.B. Song, Application of natural vegetable oil in cosmetics, Daily Chemical Science, 32(8), 4–59 (2009). (11) J. Yue, Application of commonly used thickeners in cosmetic formulations, Fragrance and Flavor Cosmetics, 44(4), 49–55 (2017). (12) L.Y. Huang, The bacteriostatic action of 4 kinds of Chinese medicine extracts and their application in skin detergents, Perfume Flavor Cosmetics, 47(4), 36–40 (2020). (13) Y.S. Wang, Evaluation of bacteriostasis effects of alcohol and water extracts of six traditional Chinese medicines on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 56(5), 62–65 (2020). (14) Z.C. Ou, Study on bacteriostatic efficacy of eight traditional Chinese medicine extracts in cream cosmetics, Daily Chemical Industry, 47(3), 148–152 (2017). (15) P.Y. Nan, Comparison of in vitro bacteriostatic test of 15 kinds of traditional Chinese medicines by water decoction and ethanol reflux extraction, Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 54(11), 50–52 (2018). (16) D. Peng, In vitro bacteriostasis activity of 40 traditional Chinese medicine extracts against 6 common clinical infectious strains, Shandong Medicine, 57(27), 27–30 (2017). (17) Y.S. Liu, “Study on Extraction and action mechanism of bacteriostasis active components of Thesium chinense.” PhD thesis, Anhui: Anhui Agricultural University. PhD thesis, (2006). (18) Y. Li, Inhibitory effect of Enshi Tengcha ethanol extract on spoilage microorganisms in high temperature cooked fish, Preservation and Processing, 21(1), 124–130 (2021). (19) J.L. Wang, The application of Angelica sinensis extract and its active ingredients in cosmetics, Perfume Flavor Cosmetics, 49(3), 101–104 (2021). (20) X.H. Li, In vitro antioxidant and bacteriostasis activities of different polar parts of daibaijie alcohol extract, Yunnan Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 42(6), 69–73 (2021). (21) S.S. Song, Study on bacteriostasis properties of extract of Radix pyrophorae, Anhui Agricultural Science, 49(12), 187–189 (2021). (22) G.P. Chen, Study on bacteriostasis activity and optimal formula of different extracts of traditional Chinese medicine, Jiangxi Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 40(3), 21–23 (2021). (23) S.C. Li, In vitro bacteriostasis test of seven traditional Chinese medicine extracts against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, Sichuan Animal Husbandry and Veterinary, 40(2), 29–31 (2013). (24) Y. Jia, The anti-inflammatory and bacteriostatic effects of Compound Radix phlei gel external preparation, Daily Chemical Industry, 50(12), 848–853 (2020). (25) Y.H. Peng, Application of oil soluble Arnebia extract in cosmetics, Guangdong Chemical Industry, 46(22), 34–35 (2019). (26) Z.Y. Wang, Research progress on chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and processing methods of Sophora flavescens, Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 53(10), 71–79 (2019). (27) G.H. Xu, Study on Flavonoids composition and antioxidant capacity in citrus peel, Food Industry Science and Technology, 36(16), 114–117 (2015). (28) D.L. Su, Overview of the functions of functional components in citrus peel, Modern Food Science and Technology, 22(2), 260–262 (2006). (29) L.Y. Zuo, “Extraction of polyphenols from the peel of citrus plants and detection of their antioxidant and bacteriostatic activities.” PhD thesis, Southwest University, (2018). (30) T.T. Sun, Effect of different extraction methods of spice essential oil on bacteriostatic effect of low temperature meat products, Agricultural Products Processing, 11(7), 83–85 (2012).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)