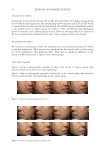
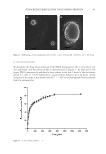
43 SUNSCREEN FORMULATION CONTAINING PROPOLIS IN VITRO RELEASE PROFILE To determine the drug release behavior of the PLGA nanoparticles, the in vitro release test was performed, and the release profile is demonstrated in Figure 3. As depicted in the figure, PLGA nanoparticles exhibited a burst release in the first 3 hours of the incubation period (i.e., 48.5 ± 3.41%), followed by a sustain release behavior up to 24 hours. At the end point of the study, it was showed that 83.7 ± 1.18% of total entrapped PFs was released from the nanoparticles. Figure 2. SEM images of the nanoparticles (A) ×4,000 1 cm = 450 nm, (B) ×20,000 1 cm = 100.6 nm. Figure 3. In vitro release profile n = 3.
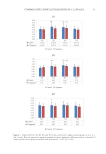
44 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE DETERMINATION OF THE SPF The results for in vitro determination of the SPF of the sunscreen samples are shown in Figure 4. As shown in the figure, sunscreen formulations incorporating propolis-containing PLGA nanoparticles exhibited significantly higher protection compared to other sunscreen formulations (p 0.05). Furthermore, as depicted in the figure, the plain PLGA nanoparticles showed only a slight photoprotection, which was significantly lower than sunscreen formulation containing free propolis. DISCUSSION According to several studies, propolis exhibits various biological properties, and its potential for wide applications in pharmaceutical and food processing industries have attracted much interest (25,28–30). Propolis is a natural substance that contains antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory compounds, and it can be incorporated in sunscreen formulations as a potential sun-protecting cosmeceutical agent (4). Various studies have identified the structure of different polar and nonpolar compounds of propolis and have characterized their biological properties (24,31,32). The lipophilic nature of the major compounds of propolis causes its low aqueous solubility and therefore the commercial formulations of propolis are mostly based on ethanol, which may be accompanied by local adverse reactions such as neurotoxic effects (33). Nanoparticles are useful drug delivery systems to elaborate the bioavailability of propolis formulations (34). Moreover, nanoparticles could protect propolis from environmental degradation and therefore enhance the stability of the formulations (20,35,36). Encapsulation of the propolis into PLGA nanoparticles has been previously studied and showed enhanced Figure 4. Determination of SPF. ***p 0.001.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)