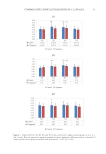
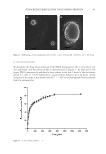
25 TESTING OF HAND CREAMS As seen in Figure 4, the inhibitory effect of C reticulata peel extract on the three tested strains increased in a concentration-dependent fashion. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of C reticulata peel extract against S aureus, C albicans, and E coli were 75 μL mL−1, 50 μL mL−1, and 15 μL mL−1, respectively. The analyzed test data are summarized in Table VI. The four bacteriostatic agents had different bacteriostatic effects on the three tested strains. Among them, L erythrorhizon extract and C reticulata peel extract had the strongest bacteriostatic effects, followed by S baicalensis extract, and S flavescens extract had the weakest effect. Optimization of plant materials. According to Table VI, the bacteriostatic effects of the L erythrorhizon extract and C reticulata peel extract were relatively strong. Therefore, the C reticulata peel extract and L erythrorhizon extract were selected for compounding to optimize the bacteriostatic effect. Various combinations of the extracts were tested, the results of which are shown in Table VII. The results showed that Compound #3 (hereafter referred Bacteriostatic agent volume ratio concentration/μL mL-1 Figure 3. Inhibitory effect of S flavescens extract on three tested strains. Bacteriostatic agent volume ratio concentration/μL mL -1 Figure 4. Inhibitory effect of C reticulata peel extract on three tested strains. OD change value OD change value
26 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table VI Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of the Four Bacteriostatic Agents Against the Three Tested Microorganisms Bacteriostatic agent Minimum inhibitory concentration (μL mL−1) S aureus C albicans E coli S baicalensis extract 75 100 100 L erythrorhizon extract 50 25 50 S flavescens extract 100 100 100 C reticulata peel extract 75 50 15 Table VII Bacteriostatic Effects of Different Composite Plant Extract Ratios Compound number Combination method Average inhibition zone diameter (mm)a C reticulata peel extract (g) L erythrorhizon extract (g) S aureus C albicans E coli 0b 0.0 0.0 0.00 0.00 0.00 1 1.5 0.0 46.20 48.44 54.86 2 1.2 0.3 46.51 49.82 55.28 3 1.0 0.5 47.83 52.63 55.94 4 0.8 0.7 47.62 53.14 54.73 5 0.7 0.8 46.85 49.85 54.11 6 0.5 1.0 45.93 48.93 53.42 7 0.3 1.2 42.48 48.25 52.53 8 0.0 1.5 42.19 47.37 51.07 a The bacteriostatic effect was determined according to the diameter of the inhibition zone (inhibition diameter: 6 mm) as described in the bacteriostatic performance test section. b Indicates no bacteriostatic agent was added rather, an equal amount of deionized water was added as a blank control. Table V Base Formula and Plant-Based Hand Cream Formulations Phase Raw material Base formula Plant extract hand cream formula A Deionized water 74.85 73.40 Glycerin 8.00 8.00 Allantoin 0.15 0.15 Xanthan gum 0.20 0.15 B Jojoba oil 5.50 5.50 Shea butter 2.50 2.50 Isopropyl palmitate 1.30 1.30 Dimethicone 2.50 2.50 Steareth-2 2.00 2.00 Steareth-21 1.50 1.50 C Tocopheryl acetate 1.50 1.50 Composite plant extract / 1.5 100.00 100.00
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)