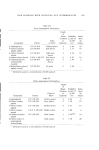
616 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table VII Meta-phenylenediamine Derivatives Mixed with p-Phenylenediamine or p-Aminophenol Compound Mixed Solution with Mixed Solution with P.P.D. P.A.P. Fades Fades After After (in (in Color on Hair a (hours) Color on Hair a hours) m-Phenylenediamine Chloro-m-phenylene diamine Nitro-m-phenylene diamine m-Toluylenediamine 2,4-Diaminoanisol sulphate 4-Methoxy-6-methyl-m-phenylene- diamine 1,3,5-Triaminobenzene trihydrochloride 2,4,6-Triaminotoluene trihydrochloride p-Phenylenediamine (alone) p-Aminophenol (alone) Blue black 42 Red with a 2 grey cast Black with a 20 Light grey 6 red cast Yellow 20 Bright 2 brown yellow Black with a 50 Dark red 16 purple east Black 50 Orange red 8 Black 46 Orange red 4 Red brown 14 Light grey 18 brown Grey brown 22 Light golden 6 Brown Dark brown 4 ...... ...... Light golden 4 brown Solutions were 0.01 M in both components. Table VIII Meta-Aminophenol Derivatives Alone and with p-Aminodiphenylamine Mixed Solution with Alone P.A.D.A. Solubility Fades at pH 9.7 Color on Hair After (g/100 (from 0.025 M Color on Compound Patent ml) Solution) Hair • hours) m-Aminophenol G.P. 210,643 3.85 No color Blue black 3,5-Diaminophenol ... 3.57 No color Red brown hydroehlorid e black Diethyl-m-amino- U.S.P. 3,216,899 0.20 Very light Dark red phenol grey brown brown p-Amino-0-eresol (4- U.S.P. 3,210,252 0.65 Golden Dark grey amino-2-hydroxy- blonde purple 1-methylbenzene) p-Aminodiphenyl- . ........ Brown black amine (alone) 28 28 5 8 14 Solutions were 0.01 M in both components.
HAiR COLORING WITH OXIDATION DYE INTERMEDIATES 617 Table IX Meta-Aminophenol Derivatives Mixed with p-Phenylenediamine or p-Aminophenol Mixed Solution with Mixed Solution with P.P.D. P.A.P. Fades Fades After After Compound Color on Hair a (in hours) Color on Hair a (in hours) m-Aminophenol 3,5-Diaminophenol hydrochloride Diethyl-m-aminophenol p-Amino-o-cresol p-Phenylenediamine (alone) p-Aminophenol (alone) Dark purple 8 Medium red 16 grey brown Red brown 4 Grey brown 14 Olive brown 5 Green brown 7 Dark red with 18 ]3right orange 18 blue east Dark brown 4 ...... ...... Light golden 4 brown Solutions were 0.01 M in both components. importance of these color modifiers in increasing the depth of shade, changing the color, and increasing the fastness to light. It is apparent that m-phenylenediamine, m-toluylenediamine, 2,4- diaminoanisol sulfate, and 4-methoxy-6-methyl-m-phenylene diamine are all equally effect'-•e i'n producing a deep blue shade of comparable light fastness. The tendency of hair dyed with oxidation colors to turn red on aging has long been a deep concern of the hair colorist. As evi- denced by references in the patent literature (9, 10) this tendency is ac- celerated by the application of acid rinses or contact of the hair with acid perspiration. Fadeometer readings are a measure of the fading of colors due to the exposure to light. However, it is doubtful if such de- terminations measure the reaction of colors to aging. Dyeings that had been made in December, 1952, using mixtures of P.P.D. and each of the four meta-compounds listed above, were found in our files. These had been stored in the absence of light and out of contact with acid fumes. Records showed that originally they were all blue-black colors of comparable depth of shade, with light fastness ratings varying from forty-two to fifty hours. Examination of these dyeings after thirteen and one-half years revealed that the one made with 2,4-diaminoanisol sulfate was still black, while that made with m-phenylenediamine was slightly red and those made with m-toluylenediamine and 4-methoxy- 6-methyl-m-phenylenediamine were very red. This indicates the need for additional tests for the control of hair dye formulations. Such tests
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)