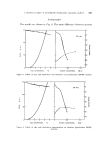
L.qPONI'TE CLAY--A SYNTHETIC INORGANIC GELLING AGENT 249 Sorbitol/water Pure sorbitol is a solid at room temperature, but it is most commonly marketed as a syrup of 70% concentration. Dilutions were made from this syrup, but the concentrations recorded are of the pure chemical. Fig. 11 shows the ESS values. The OD values could not be measured, owing to bubble inclusion, but the broken line indicates a visual estimate. 150,•,•......_. , I00 50-- I clay •--- Estimated visually -io -- :•0 -- 30 , -- 40 'o .-- -- 50 0 -- 60 I I I 0 • 2 3 4 5 0 0.5 1.0 Clay concentration, % Sodium cancentratian, meg -I Figure 11 Effect of clay and electrolyte concentration on sorbitol/water (56/44) systems All yield values are again higher than in the previous systems studied. The effect of electrolyte addition is not clearly indicated, but as the actual yield value is very high, even at the highest sodium chloride addition used, we can assume that this system has the highest electrolyte tolerance of all the studied organic solutions. Water For comparison, the behaviour of Laponite CP dispersed in distilled water is shown in Fig. 12. As expected, the yield values are the lowest for all clay concentrations, and the electrolyte tolerance is the highest. PLASTIC VISCOSITIES Although the main interest of this paper is structure formation in
250 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 150 100 Clay concentration, % 0 0.5 1.0 Sodium concentrotion, me g-• Figure 12 Effect of clay and electrolyte concentration on pure water systems liquids, the plastic viscosities of all the dispersions made were also measured. The results in Tables III -- V show that in all cases the plastic viscosity greatly increases with increasing clay concentration, but is less affected by variations of electrolyte or organic content. Table III Effect of clay concentration on plastic viscosity (cP) System 40 •o Methanol 25 •o Methanol 40 •o Ethanol 25 •o Ethanol 40 % isoPropanol 25 % isoPropanol 40 •o Acetone 50 •o Ethylene glycol 60 •o Glycerol 50 •o Sorbitol Water 1.6 1.2 4.3 13.9 17.5 0.8 Clay concentration 3.7 3.0 5.1 4.6 6.3 4.4 4.3 6.6 16.1 24.4 2.3 5.4 4.8 7.0 6.3 8.7 7.8 5.8 8.6 18.5 30.2 5.1 7.0 10.3 -- -- -- -- __ 10.2 8.8 10.2 29.0 41.7 5.9
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)