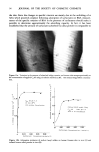
j. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 31, 45-66 (March/April 1980) Comparative study on the mechanism of irritation by sulfate and phosphate type of anionic surfactants GENJI IMOKAWA, Tochigi Research Laboratories, Kao Soap Co., Ltd., 2606 Akabane, lchikaimachi Hagagun Tochigi 321-34, Japan. Received May 25, 1979. Synopsis Monoalkyl phosphates of high purity were synthesized and investigated for their surface active properties and cutaneous effects. It has been found that these surfactants possess adequate surface active properties similar to those of common ANIONIC SURFACTANTS and that they exhibit considerable safety on the skin in comparison with typical anionic surfactants used commercially. In addition, the low irritating effect was investigated with respect to their effect on various biological systems including protein, enzyme, and lysosome membrane. Our results indicated that a remarkably weak membrane rupture effect at a concentration less than critical miceIlar concentration was important for the low irritating feature. MECHANISMS by which IRRITATION is caused by surfactants were discussed in the comparison of MONOALKYL PHOSPHATE and SODIUM DODECYL SULFATE. INTRODUCTION Monoalkyl phosphate (MAP) type of surfactants (Figure 1) are anionic surfactants in which the terminal groups, SO 3- or OSO3-, usually found in anionic surfactants is replaced by OPO 3- in order to enhance its safety on human skin. The critical micelie concentration (cmc) value and surface tension of a typical MAP i.e., C•2MAP monosodium salt was respectively 3.5 x 10 -3 mole/1 and 27.5 dyne/cm (1). Thus, surface active properties were similar to those of sodium dodecyl sulfate (C•2AS). However, as will be mentioned later, MAP possesses a remarkably weak irritating effect on human skin in contrast to high irritancy of commercially used anionic surfactants like Cx2AS. In the present report, surface active, cutaneous and biological properties of MAP and various anionic surfactants, especially C•2AS , are compared in order to gain detailed information concerning the mechanism of irritation caused by surfactants. FOAMING PROPERTIES The effect of concentration on foaming properties at 40øC of MAP monosodium series having different alkyl chain length are shown in Figure 2 (1). As expected from 45
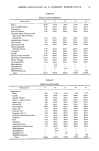
46 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS MONO ALKYL PHOSPHATE MONO SODIUM SALT ,OH C N H2N+i0-P =0 {]-NA + N=I2 KRAFT POINT: 31,5 oe M C : 3,5 x I0 -3 MOLE/L MINIMUM SURFACE TENSION 27.5 DYNE/CM ALKYL SULFATE SODIUM SALT o C N H2N+i =0 {5-NA + N=I2 C M C : 7,2 x I0 -3 MOLE/L MINIMUM SURFACE TENSION 32,0 DYNE/CM Figure 1. Surface active properties of monolauryl phosphate mono-sodium salt and lauryl and sulfate sodium salt. 300 200 • 100 Figure 2. Foam height-concentration curve of monoalkyl phosphate monosdium salts measured by the Ross and Miles method.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)