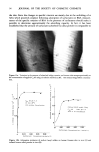
J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 31, 67-84 (March/April 1980) Decomposition of surface-active agents by bacteria isolated from deionized water YOUJI WACHI, MITSUO YANAGI, HAKUJI KATSURA and SABURO OHTA, Shiseido Laboratories, 1050 Nippa-cho, Kohoku- ku, Yokohama- shi, 223 Japan. Received May 21, I979. Presented at Annual Scientific Seminar, Society of Cosmetic Chemists, May 1979, Dallas, Texas. Synopsis Microorganisms found in deionized water used to manufacture cosmetics products, were investigated utilizing the spread-plate technique with casein-peptone-starch medium. Bacteria in the range of 10 to 100,000 per ml were found in DEIONIZED WATER storage tanks. Most of these bacteria were characterized as gram-negative, aerobic, non-spore-forming motile bacilli and identified as the genus Pseudomonas. Pseudomonas sp. 77801 was found to grow rapidly to a level of about 106/ml in deionized water and to decompose polysorbate-20. It was also found that a clear toilet water became hazy as a result of the DECOMPOSITION of the SURFACE-ACTIVE AGENT used, due to contamination with the bacteria. Our attention was directed to enzymatic decomposition by Pseudomonas sp. 77801. Although the strain was found to be killed at 60øC in 5 rain, the crude enzyme remained active even after heating at 80øC for 10 min. In addition to polysorbate-20, the crude enzyme was found to decompose the other ester-type surface-active agents. INTRODUCTION Water occupies an important role as one of the principal ingredients of cosmetics and toiletry products. For example, toilet waters are made of more than 80% water, creams 40-80% and lotions 60-80%. In order to remove organic and inorganic substances found in natural water supplies, the water used in cosmetics usually goes through ion exchange treatment or distillation. But this purified water is easily contaminated with various microorganisms (1,2) and it has been reported that contamination in cosmetics is frequently due to water-borne bacteria (3,4). Ultraviolet (U.V.) irradiation is usually employed to control microbial growth in treated water, but is not considered to be absolute. Although contaminated purified water poses various problems with its use, the work in this area has not received much attention. Development of a haze, a kind of deterioration of a toilet water, gave a clue to our present work. First, we isolated the bacteria considered to be indigenous to deionized water, and studied their behaviors and characteristics. It was found that a toilet water became hazy because of the 67
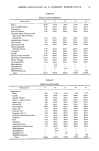
68 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS deterioration of solubilizers, unless the sterilization of the purified water to be used was well controlled. MATERIALS The surface-active agents (S.A.A.) used were obtained from Nihon Emulsion Co., Ltd. and Nikko Chemical Co., Ltd. Steapsin (lipase) was obtained from Tokyo kasei Kogyo Co., Ltd. All other chemicals used were of reagent-grade quality. METHODS THE ISOLATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BACTERIA Viable counts in purified water were performed in casein-peptone-starch (C.P.S.) agar (7) using the spread-plate method with sterile deionized water as a diluent. The composition of this medium is given in Table I. All the plates were incubated at 25øC for 7 days before counting. THE DECOMPOSITION OF S.A.A. Test organisms were inoculated into the sterile tubes containing 5 ml of 0.1% S.A.A., and were incubated at 25øC for 3 weeks. The haziness was used as a measure to judge the degree of the decomposition of S.A.A. THE CONFIRMATION OF THE HAZY PHENOMENON OF LOTION A Lotion A was used to examine haziness due to bacterial contamination. This lotion contains 10 ml 95% ethyl alcohol, 1 ml glycerol, 0.1 g methylparaben and 100 ml sterile aleionized water. Table I Composition of Medium CPS and Nutrient Agar Ingredients(g/I) Nutrient Agar CPS '1 Agar Meat Extract 7.0 Peptone 10.0 0.5 NaCI 3.0 Soluble Casein 0.5 Soluble Starch 0.5 K2HPO4 0.2 MgSO4.7H20 0.05 FeCI3 trace '2 Glycerol 1.0ml Deionized Water 1000ml 1000ml Agar 20 20 pH 7 7 '1 Casein-peptone-starch (CPS) medium (by Collins and Willoughby) *24 drops of a 0.01%solution
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)