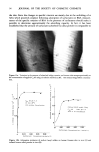
SKIN IRRITATION BY ANIONIC SURFACTANTS 57 To determine the potential of MAP to remain adsorbed on skin, this technique was applied. The results (Figure 14) showed a similar staining for MAP to that of water-treated control, and higher staining intensity than ES, suggesting that MAP is less adsorptive onto surface layers of skin. SKIN IRRITATION Figure 15 shows the results (15) of cutaneous reaction for a variety of anionic surfactants after a 24-hr closed patch test on the human forearm at 1.0 g/lOOml. It is clear that most anionic surfactants possess marked irritating effect on human skin at this concentration. On the other hand, in similar experiments using MAP (Figure 16), although the MAP's produce varying degrees of irritation depending on alkyl chain length or salt type, two typical types of MAP, C•2MAP monosodium and mono- triethanolamine salts, gave no cutaneous reaction even at 2.0 and 4.0 g/lOOml (1). On the basis of these findings, it is concluded that, in general, MAP has a very low irritation potential as compared to typical anionic surfactants used commercially. Subsequently, the low irritating effect of MAP-type surfactants at higher concentra- tions was confirmed in animal studies (16). Figure 17 shows irritancy of C•2MAP mono-TEA salt, a typical type of MAP, as a function of the concentrations in comparison with C•2AS. The elicitation of irritation with this compound required a concentration of more than 4 g/100 ml, whereas C•2AS produced an irritating response even at 0.05 g/100 mi. After occlusive application of 2 g/lOOml of C•2AS, a marked irritation accompanied by crusta was observed, whereas C•2MAP produced a similar ClO C12 C12 C14 C16 C12 C12 C12 C12 C12 C12 C12 C12 M A P AGS IE4 O AS SOAP E3S LASAOSSAS Na Na TEA Na Na Figure 16. Cutaneous reaction of MAP following 24 hr closed patch test on human skin. Clinical diagnosis was carried out 2 hr after removal of closed patch. MAP: monoalkyl phosphate, AGS: alkyl acylglutamate, EO: alkyl polyoxyethlene, AS: alkyl sulfate, Soap: sodium carboxylate, ES: alkyl ether sulfate, LAS: linear alkyl benzene sulfonate, AOS: alfa-olefin sulfonate, SAS paraffin sulfonate.
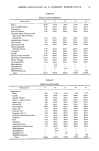
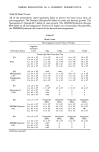
58 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 5.0 mono TEA CI2AS / / 2:0 l.O 0 -. 0 lO.O 2 .0 30.0 $urfactant Concent r a t ion (g/lO0 ml) Figure 17. Comparison of irritations following 24 hr closed patch test on guinea pig skin using C12MAP monoTEA salt and C12AS dissolved at various concentrations. •2 3 C12 A 0 • ' 23456789 123456789 1 23456789 0•5[ C8MANamonoCIo123456789Namono 123456789 0•5[ CI2MANaMAC14mono123456789Namono 123456789 C16 MAP C18 MAP mono Na mono Na 123456789 123456789 Treatment Number Figure 18. Cumulative irritancy of series of monoalkyl phosphate monosodium salts at the 2.0% concentration as compared to typical anionic surfactants. AS: alkyl sulfate, ES: lauryl ether sulfate, AGS: lauryl acylglutamate.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)