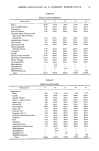
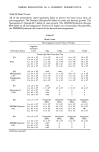
SKIN IRRITATION BY ANIONIC SURFACTANTS 47 300 --200 .. •1oo I •4 1 3 3 1 •2 I •1 I C o,nc. (mole/ I ) Figure 3. Foam height-concentration curve of alkyl phosphates with several alkyl and salt types in comparison with C•2AS. C12mono-salt: CuMAP mono-sodium salt Cusesqui-salt: CuMAP sesqui-sodium salt Cudi-salt: CuMAP di-sodium salt sesqui-alkyl: sesqui-Cualkyl phosphate. its surface active properties, MAP monosodium salts, except C•6MAP, reveal a foaming power equal to alkyl sulfate, with the highest power in CuMAP. There are three major type of salts in MAP, namely mono-, sesqui- and di-salts, and their foam properties are shown in Figure 3. It can be seen that the mono- and sesqui-salts possess a good foaming power similar to that of CuAS, whereas the foam produced by the di-salt or the sesqui-alkyl derivative is relatively unstable and low in its foam height. Weight % IOO AOS •so m --LAS 0 0.5 1.0 3.0 C0nc. (%) uv% lOO[ •*•AOS 0 0.5 1.0 3.0 Conc. (%) Figure 4. Defatting potency of various common anionic surfactants shown by a decrease in both oil weight and absorbance of Sudan Black dye after washing for 10 min at 37øC. AS: sodium dodecyl sulfate, LAS: linear alkyl benzene sulfonate, AOS: alfo-olefin sulfonate, ES: dodecyl ether sulfate.
48 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS © C12 AS ,• C12 MAP TEA • C10MAP mono Na ß C12 MAP diNa ß C12 MAP mono Na o C•8 MJ•P mono Na m lOO -- o 30rain at 4ffC 300 rpm UV (7ø lOO • 5o ß o o 0 0,2 05 10 0 (SAAV.) 30min at 40øC 1300 rpm 0.2 0.5 1•0 (SAA*/) Figure 5. Comparison of defatting potency of variety of monoalkyl phosphates to C•2AS. MAP: monoalkyl phosphate DEFATTING POTENCY In order to determine the defatting potency of surfactants, a mixture including triolein, cholesterol, squalene, palmitic acid and Sudan Black-acidic dye deposited on glass slides was employed as a substitute for oily soil. Six slides in a plastic holder were placed in a beaker with a stainless steel propeller at the center. Washing was carried out with 900 ml of surfactant solution for 10 and 30 min at 40 _+ iøC and at 1300 _+ 50 rpm. To find out the suitability and applicability of this system, typical anionic surfactants such as AS, LAS, AOS and ES were tested. Since the results (Figure 4) were comparable to the known order (2) of defatting ability of these surfactants as checked by both UV and weight methods, the washing system was reliable and convenient. Figure 5 shows defatting potency of the MAP (1). It was found that MAP's at low concentration of about 0.2% possess low defatting potency, but at higher concentra- tion of about 1.0% increase to as high a level as that of C•2AS, especially in Cx2MAP mono-TEA salts. SKIN ROUGHNESS Skin roughness properties of MAP were evaluated in vivo by our circulation method (3,4) in which the inner surface of the forearm was roughened by contact with surfactant solution circulated by a specially designed apparatus with three glass caps, three bottles containing 150 ml of 1.0% surfactant solution and a circulator equipped with three pumps connected with silicon rubber tube. Figure 6 shows abnormal scaling and dryness of forearm skin induced after four cumulative treatments of C•2AS
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)