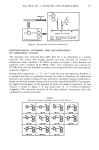
D&C RED NO. 9 ANALYSIS AND PURIFICATION 277 fi-naphthol to give D&C Red No. $, which is converted to the barium salt, D&C Red No. 9. The desulfonation reaction hardly seems possible in this process. Accordingly, it seems likely that the confirmed subsidiary colors are produced from the aromatic amine impurities contained in Red Lake C Amine and fi-naphthol. In order to prepare the standard samples for the quantitative analysis and the contact sensitization test of the subsidiary colors in D&C Red No. 9, nineteen kinds of both subsidiary colors, the structural formulae of which had been confirmed, and related compounds were synthesized (Table II) as standard samples. Each aromatic azo compound was synthesized from the corresponding amine and fi-naphthol. When pertinent aromatic amines were not commercially available, the aromatic nitro- compounds were reduced to aromatic amines which were used for raw materials. The synthesized aromatic azo compounds were purified by recrystallization using acetone, and their structural formulae were confirmed by GC-MS, NMR, etc. The subsidiary colors in various samples of D&C Red No. 9 were quantitatively analyzed. As shown in Figure 4, D&C Red No. 9 was dissolved in 1% (V/V) sulfuric I D&C Red No.9 0.05g I (Weigh exactly) :::::.....:• ( Dissolve with 1% sulfuric acid/DMF, 25ml • Add water, 75ml Pass this solution through SEP-PAK C,8 cartridge using 100ml syringe Wash with 50r•l water Elute with 5m• acetone and then 20ml chloroform •.•Evaporate to iryness with rotary evaporator(•Te-'-•p..'•025•--•m,methanol ( Add 150,--,200/zl 100ml syringe IHPLC-]]]:I Col"•-'•mn TSK LS-41• ":•+-SEP PAK C•8 Eluent : Methanol, 1.5ml/min. • cartridge Detector: VIS (436nm), 0.5AUFS -] r Inj. vol.: ca. 150p. I •) 5 •10ml/min. I I I Fractiøn All Fraction B I I I I IFraction C I IFraction D I I I Evaporate to dryness - Add 1% ethyl acetate/n-hexane. 1.00ml Column : Nucleosil-50*, 4mm i.d.x 25cm, Temp.: 30øC Eluent : 1.0% ethyl acetate/n-hexane, 2.0ml/min. Detector: VIS (436nm), 0.01 AUFS , Macherey-Nagel (GER) Figure 4. Flow chart for determination of subsidiary colors in D&C Red No. 9.
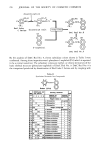
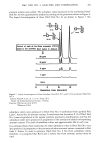
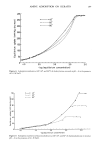
278 .JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS acid/N,N-dimethylformamide the solution was passed through a SEP-PAK C•8 cartridge (Waters Co.) to adsorb the subsidiary colors, and then the subsidiary colors were eluted with the solvent. First, the eluted matter was roughly divided into the following four fractions (A • D) under condition III by HPLC: (P-0) was collected in fraction A, (P-1 - P-6, P-9 - P-10) in fraction B, (P-7 • P-8, P-11 • P-15) in fraction C, and (P-16 • P-18) in fraction D. Secondly, each fraction was separated and quantitatively analyzed under condition IV by HPLC. The average recovery by this procedure was approximately 80%. The results are in Table III. All eight D&C Red No. Table III Determination of Subsidiary Colors in Commercial D&C Red No. 9 [ppm•] Sample No. P-0 P-6 P-7 P-9 IP-12 P-13 P-14 P-15 P-16 P-17 P-18 Total I m 0.7 m 0.5 • 32. 42. 2.9 1.6 • 13.1 2 1.0 • 0.5 0.7 4.4 0.7 0.8 4.4 1.0 0.7 • 142. 3 • 7.4 m -- 19.0 4.6 !3.6 22.4 1.7 68.7 4 0.5 2.1 • • 3.7 0.9 1• 1.0 • 10.0 . 5 7.5 1.3 27.1 1.7 t0'4 14.8 10.2 6.5 1.8 71.3 6 5.1 • 1.0 1.5 22.1 2.4 -- 12.7 8.2 4.2 1.3 58.5 7 4.7 8.9 1.1 I • 6.1 6.2 1.8 1.3 30.1 8 14.8 m 3.5 • 5.2 3.4 1.3 24.8 20.0 7.0 3.9 83.9 m: not detected 1-3. Manufacturer A (Japan): Straight color 4. Manufacturer B (Japan): Straight color 5-7. Manufacturer C (USA) : Extended toner (Substratum: Barium sulfate) 35% pure dye 8. Manufacturer C (USA) : Extended toner. 87% pure dye 9 samples contained some subsidiary colors.,P-12, P-15, P-16, and P-17 were contained in all of the samples. The total amounts of the subsidiary colors ranged from several ppm, at the lowest, to approximately 80 ppm at the highest. IDENTIFICATION AND QUANTIFICATION OF IMPURITIES IN AND PURIFICATION OF RED LAKE C AMINE Since the unsulfonated aromatic amine impurities contained in Red Lake C Amine were regarded as the source of the subsidiary colors in D&C Red No. 9, the following procedure was carried out: 1) identification of impurities in Red Lake C Amine 2) quantification of unsulfonated aromatic amines in Red Lake C Amine and 3) purification of Red Lake C Amine. 1. IDENTIFICATION OF IMPURITIES IN RED LAKE C AMINE Red Lake C Amine was dissolved in sodium hydroxide solution and chloroform was added to extract the non-acidic impurities. The structural formulae of the extracted impurities were confirmed by GC-MS. It was found that many aromatic amines were contained in Red Lake C Amine, as shown in Figure 5.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)