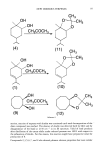
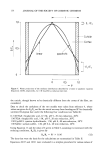
142 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS one sunscreen. This synergistic trait of sunscreens is common knowledge, but within the cosmetic industry, only a few combinations are utilized. The following experiments show that there are more combinations of sunscreens avail- able that are capable of achieving medium-to-high SPF values than were previously believed to exist. MATERIALS AND METHODS TEST LOTIONS A simple anionic lotion was used for the test vehicle, (Table I). The percentages of sunscreens were subtracted from the water. Finsolv TN was selected as the primary oil of the oil phase because of its ability to solubilize sunscreens (5). Both padimate O and octyl methoxycinnamate were tested with combinations of oxybenzone at 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6%, with octyl saliclyate at 2, 3, 4, and 5%, and with homosalate at 4, 6, 8, and 12%. TEST PROCEDURE The SPF testing was performed using the FDA-proposed method. A 150-watt xenon arc lamp Solar Simulator from the Solar Light Company was used as the light source. Eight subjects with skin types ranging from II to IV, and without any previous tan, were used. Eight subjects instead of the suggested 20 were used to reduce the time involved. An accurate trend is usually apparent by the eighth subject. RESULTS The SPF values for each combination can be seen on Table II. The graphs representing these results are in Figure 1. Table I Lotion Base Used for All Tests Test formulation Ingredient Percent Water Carbomer-940 Methylparaben Propylparaben Tea Amphisol FinsolvTN Stearic acid Cetyl alcohol Q.S. 0.15 0.30 0.10 1.00 3.00 10.00 4.00 1.50
SUNSCREEN COMBINATIONS AND SPF 143 Table II Table of SPF Values and Cost/SPF Ratios of Test Lotions Percent Additive Average Standard Cost/SPF sunscreen sunscreen SPF* deviation Cost ratio 7.5% PAD. O + 2% OXY 18 2.56 4.53 4.04 3% OXY 19 2.43 4.91 3.85 4% OXY 23 4.48 5.57 4.07 5% OXY 23 4.44 6.23 3.69 6% OXY 28 5.39 6.89 4.10 2% O.S. 16 3.14 3.46 4.55 3% O.S. 15 2.39 3.73 4.07 4% O.S. 18 3.59 4.00 4.40 5% O.S. 21 3.65 4.27 4.86 4% HMS 16 2.66 3.64 4.30 6% HMS 15 2.39 3.99 3.81 8% HMS 18 3.43 4.34 4.17 10% HMS 20 3.15 4.70 4.16 12% HMS 22 3.19 5.05 4.42 7.5% CINN + 2% OXY 21 2.27 5.62 3.77 3% OXY 20 3.07 6.28 3.26 4% OXY 22 3.88 6.94 3.20 5% OXY 19 5.09 7.60 2.47 6% OXY 23 4.89 8.26 2.79 2% O.S. 15 2.93 4.83 3.16 3% O.S. 17 3.31 5.10 3.35 4% O.S. 18 2.71 5.37 3.34 5% O.S. 18 3.47 5.64 3.20 4% HMS 16 1.82 5.01 3.28 6% HMS 16 2.68 5.36 2.90 8% HMS 19 2.45 5.71 3.38 10% HMS 17 1.88 6.07 2.78 12 % HMS 20 4.04 6.42 3.14 Abbreviations: OXY, oxybenzone O.S., octyl salicylate HMS, homosalate PAD. O, padimate O CINN, octyl methoxycinnamate. * The SPF testing procedure is performed by using a 25% plus or minus exposure range. Therefore the accuracy of each result has a 25% error factor. The listed SPF values are an average of these results. DISCUSSION SPF VALUES The combinations using oxybenzone yielded the highest SPF numbers. However, within the mid-SPF ranges (15 to 21), all the test materials performed well. Padimate O yielded the highest SPFs for each of the maximum concentrations. With lower con- centrations of the additives, the octyl methoxycinnamate combinations yielded the highest SPFs. COST EFFICIENCY Dividing the chemical cost of the lotion by its SPF value determines a cost ratio for each
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)