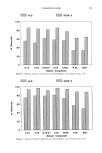
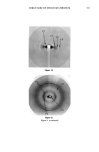
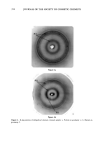
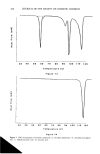
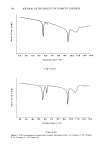
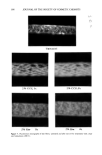
350 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Stratum Corneum Proteic Scattering Components Group d (•) Aspect Intensity P ! 125 // Equatorial diffuse zone vs 125 // Equatorial diffuse zone vs 86 // Equatorial diffuse zone vs P2 9.4 // Equatorial sharp arc vs 4.7 // Equatorial sharp arc s 3.15 // Equatorial sharp arc w P3 9.5 //3, Nonisotropic broad band vs 4.58//l Isotropic broad band s Intensity: vs, very strong s, strong w, weak. size of a diffracting object from the sharpness of the arc). This protein would appear to have a planar structure of type 13, as the value of 9.4 • is typical of the inter-chain distance of type-13 forms (12). It is also difficult to determine the origin and nature of this protein constituent, which has previously been reported by White in the SKH mouse SC. The size of the dif- fracting domain is, however, larger than that of the intercellular spaces this would suggest that the protein is an intracorneocyte protein such as filaggrin, which has a partial 13 structure. However, the desmosome remnants are situated in dilated zones of the SC, and such an origin cannot be excluded for this unidentified molecule. The confirmation of this hypothesis would be very important given the cohesive role of these elements between corneocytes. Figure 2a Figure 2. X-ray patterns of normal stratum comeum sample: a. Pattern in geometry 3_ b. Pattern in geometry// c. Pattern in geometry//.
STRUCTURE OF STRATUM CORNEUM 351 Figure 2b Figure 2c Figure 2 (continued)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)