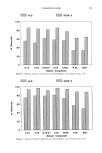
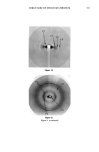
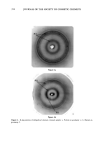
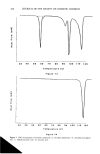
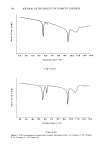
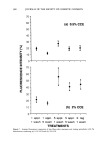
ANTI-IRRITANTS AND TANNING ACCELERATORS 371 ening in response to UV irradiation. L* values are used for measurement of skin light- ness. For a complete picture of the tanning response, AE* can be calculated as follows: A E* = X/(A L*) 2 q- (A a*) 2 q- (A b*) 2 AE* then represents the linear combination of changes in both skin reflectance as well as color. In the following studies skin tanning was assessed visually as well as with L* values measured by the chromameter. The MED for each panelist was determined to obtain the optimum UV dose for the experiment. Tanning products were applied on the skin before or after exposure to the solar simulator, at the appropriate UV dose levels. Twenty-four-hour erythema was measured by a* values, and after 48-72 hours tanning was determined by the change in L* values as compared with the control site exposed to the same dose of UV irradiation but not treated with tanning accelerator. Visual evalua- tion of tanning was conducted by a panel of trained judges on a 1-4 standardized scale. The results were evaluated with a statistical package (Statgraphics) to assess signifi- cance. RESULTS ERYTHEMA ASSESSMENT Correlation of instrumental and visual assessment. In order to determine if the results ob- tained from the chromameter measurements were in agreement with those obtained from visual assessment, we determined the correlation coefficient for results obtained via both measuring techniques (Table I). After subtracting the baseline skin measurements, the product-treated site values were subtracted from the a* value of the untreated site to obtain Aa* value (Table II). Visual scoring of skin erythema, as grade 1 to 4, based on a standardized scale, was done by a panel of trained observers and compared with the Aa* values obtained with the chromameter (Figure 1). The visual grading of skin erythema is generally consid- ered the difference between baseline skin color and increase in redness as observed by the eye. We found a significant correlation (r = 0.6785, p 0.001) between values obtained on increase of redness and visual grading of skin erythema. Anti-irritancy studies. The efficacy of an anti-irritant challenged by either a chemical or physical stimulus was determined in terms of inhibition of erythema (a* value) and compared with the skin area treated with irritant alone. Figure 2 shows two sites treated with the chemical irritant Balsam of Peru. Site B is a control that was not Table I Correlation Between Visual Scoring and Chromameter Readings for the Measurement of Skin Erythema Chromameter Visual Correlation grading A a* grading coefficient r n = 14 3.29 1.! 0.6785 (p 0.00!)
372 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II Anti-Irritancy Effect of Product Baseline Treated Control skin color site A site B a* Values 8.65 9.29 13.55 A a* 0.64 4.9 % Decrease in erythema 86.94% pretreated with the prospective anti-irritant. Site A, on the other hand, was treated with the anti-irritant material at a dose of 2 mg/cm 2, 20 minutes prior to application of the irritant. As illustrated in Table II, the efficacy of the anti-irritant in this case is quite clear. Chromameter measurements of both sites were obtained (1) prior to appli- cation of the irritant (baseline) and (2) after development of maximal erythema. Several measurements were taken in order to insure reading the reaction at its maximal point, which occurs about 30-40 minutes after application of the irritant. In addition, at each time point five to six replicates of each measurement were obtained. For the most part, the variance of the replicates is about 0.11 however, if the skin is blotchy, the variance increases slightly (0.18). Therefore, eight to ten replicates were obtained for each mea- surement. As illustrated in Table II, it is possible to quantify the efficacy of a prospective anti-irri- tant ingredient by evaluating the difference in erythema after subtracting baseline values. 4O MeBBuPemen• o• Erythema with CH•IOMAMETEI• ' ' I ' ' ' I ' ' ' I ' •.• •.• 3.=• vJ. su• 1 Figure 1. Erythema: Correlation between visual measurements and chromameter a* values. I I
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)