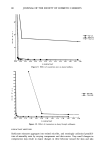
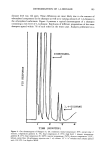
DETERMINATION OF 1,4-DIOXANE 101 Studies were performed to determine the linear range and recovery of the method. 1,4-dioxane standards were prepared at levels between 1 and 250 ppm and analyzed. The results are graphically presented as FID response vs ppm 1,4-dioxane in Figure 1. The area/concentration curve showed a correlation coefficient of 0.9998, indicating linearity over the concentration range examined. Since we were unable to obtain a 1,4-dioxane-free shampoo that contained ethoxylated surfactants, standard addition experiments were performed on two different shampoos to determine the linearity and recovery of the system. One of the shampoos (Shampoo B) contained ethoxylated compounds, while a second shampoo (Shampoo K) contained no ethoxylated surfactants. A spiking solution of 250 ppm 1,4-dioxane in water was prepared and different volumes were spiked into samples of both shampoos. These samples were then prepared and analyzed according to the procedure outlined previ- ously. The resultant data is graphically displayed in Figures 2 and 3. Shampoo B had a linear response over the spiking range of 0 to 40 ppm, with a correlation coefficient of 0.9996, and providing an intercept of 13.8 ppm 1,4-dioxane. This result compares favorably with an independent analysis of the same sample, which determined the level of 1,4-dioxane in Shampoo B to be 13.0 ppm. As shown in Figure 3, analysis of Shampoo K, the ethoxylate-free shampoo, was linear over the spiking concentration range of 7 to 225 ppm 1,4-dioxane, with a correlation coefficient of 0.9999 and an intercept of 1.5 ppm. This also compares favorably with an independent analysis that determined the level of 1,4-dioxane in Shampoo K to be 1.3 ppm. The recovery of the 20O 100 o -50 ß . 0.9999 I ' I ' ! 50 150 250 PPM DIOXANE SPIKED Figure 3. Standard addition of 1,4-dioxane into Shampoo C.
102 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II Recovery of 1,4-Dioxane Spiked Into Shampoo K and Shampoo B 1,4-Dioxane 1,4-Dioxane added (ppm) found (ppm) % Recovery Shampoo B Shampoo K 0 13.0 N.A. 9.3 22.0 98 14.4 27.2 98 21.2 33.4 94 38.9 51.1 94 0 1.5 N.A. 5.7 7.5 104 18.1 19.3 98 3O.2 33.6 105 91.9 98.1 105 164.0 173.6 105 216.3 229.6 105 spiked 1,4-dioxane from both shampoos is shown in Table II. The results indicate that the recovery of 1,4-dioxane from these shampoos is between 94 and 105%. This vari- ability is most likely due to the difficulty in accurately analyzing compounds at such trace levels. SAMPLE ANALYSIS Thirteen shampoos were purchased on the open market and analyzed for 1,4-dioxane content by this method. All but one of the shampoos indicated at least one ethoxylated compound on its list of ingredients. One shampoo (Shampoo K) was chosen due to the lack of any ethoxylates among its ingredients, and was used as a blank. The results of the analysis of these shampoos are presented in Table III. As can be seen, there is great variation in the level of 1,4-dioxane present in shampoos containing ethoxylated sur- factants. The lowest level of 1,4-dioxane found was 6 ppm, while the highest 1,4- Table III Levels of 1,4-Dioxane Found in 13 Shampoos Shampoo 1,4-Dioxane (ppm) A 6 B 13 C N.A. D 144 E 53 F 16 G 112 H 7 I 67 J 39 K 1 L 42 M 47 N.A.: Not analyzed due to chromatographic interferences.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)