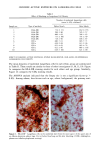
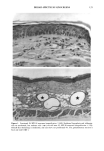
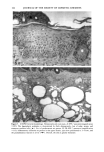
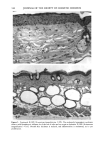
BROAD-SPECTRUM SUNSCREENS 13 5 Figure I. Continued. E: SPF-18 sunscreen (magnification x460). Epidermal hyperplasia and inflamma- tion are moderated, but sunburn cells (--•)are still seen. F: SPF-18 sunscreen (magnification X 115). Overall skin thickening is moderated, and cysts have not proliferated (*). The granulomatous reaction is focal and mild (--•).
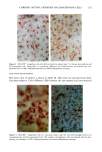
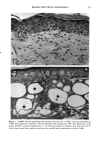
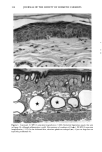
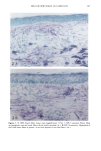
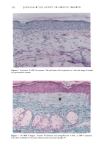
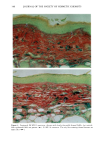
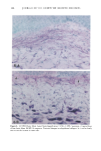
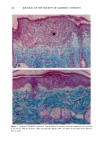
136 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS mens also had foci of very fine but densely deposited elastic fibers. A mild tinctorial change, in which the pale lavender color of collagen bundles become pink, was noted in scattered areas of the subepidermis. Mast cells were focally increased. SPF-16 sunscreen. Elastic fiber changes were similar to, but milder than, those seen with the SPF-7 sunscreen. Hyperplasia was mild to moderate, with somewhat less thickening of the fibers (Figure 2B). There were fewer foci of fine fibers and little or no tinctorial changes in collagen. SPF-18 sunscreen. Elastic fiber hyperplasia ranged from within the normal range to mild (Figure 2C). Thickening of fibers was minimal. Foci of fine fibers were less abundant and less dense. There was no tinctorial change in the collagen. With SPF-16 and -18 sunscreens, mast cells were not noticeably increased and were mainly located just above and amongst the cysts and granulomatous reaction. MASSON'S TRI-CHROME STAIN FOR COLLAGEN SPF-7 sunscreen. Loss of affinity for the collagen-specific stain occurred in several small foci in the uppermost dermis (Figure 3A). In many areas, collagen bundles were large and ropelike and without clear outlines. SPF-16 sunscreen. No reduced staining was seen with Masson's stain, but collagen bun- dles in a few areas were large, ropelike, and without clear outlines (Figure 3B). SPF-18 sunscreen. The collagen appeared normal and showed no loss of affinity for the stain (not shown). MOWRY'S COLLOIDAL IRON STAIN: GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS SPF-7 sunscreen. More than half of the specimens had a moderate increase in glycosami- noglycans (GAGs), with foci of stippled blue deposits extending across most of the specimens (Figure 4A). Two specimens had only a mild focal increase, whereas one had intensely stained deposits that extended deeply into the upper dermis. Focally dense deposits of GAGs were occasionally seen at the dermal-epidermal junction. Focal in- creases in intercellular epidermal GAGs were present in all specimens. SPF-16 sunscreen. Stippled GAG deposits were mild and focal. Areas between foci had barely perceptable traces of GAGs. In two specimens, GAGs were moderately to greatly increased. Intercellular epidermal GAGs were focally increased in most specimens (Fig- ure 4B). SPF-18 sunscreen. GAG deposits were minimal, with most specimens having either none or very mild focal deposits that were within the range of normal (Figure 4C). Intercel- lular epidermal GAGs were mild and more focal than in the other two groups. 16 Minimal Photoaging Doses of Solar-Simulating Radiation HEMATOXYLIN AND EOSIN STAIN: GENERAL MORPHOLOGY SPF-7 sunscreen. All specimens showed photodamage greatly exceeding that found with 10 MPDs. The epidermis increased to 7-9 cell layers, with numerous thicker down-
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)