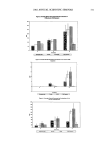
2002 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 3 ! 3 SUBSTANTIATION OF BROAD SPECTRUM & UVA RADIATION ATTENUATION CLAIMS FOR TITANIUM DIOXIDE Art Georgalas and Elizabeth Kasprzyk Tri-K Industries, Inc., Northvale, New Jersey 07647-0128 UVA sunscreen substantiation has been a contentious issue since FDA and the industry first decided to address it separately from the sunburn preventing conventional sunscreens governed by the original OTC Sunscreen Monographs. The chronic effects of long-term UVA exposure display as visible signs of aging and possibly increased incidence of some skin cancers. A reproducible bioassay to give immediate assessment of UVA attenuation can only be made with effects that are acute or instrumental methods that simply measure the light flux efI•cts. One acceptable in vivo method is the measurement of the effects on persistent pigment darkening (PPD) compared to untreated skin. In vitro broad-spectrum capability is demonstrated by identification of the critical wavelength of subject product. This is the wavelength at which the area under the absorbance curve beginning at 290 nm is 90% of the total solar UV irradiance as measured instrumentally from 290-400 nm. Additionally, instrumental measurement can estimate a UVA protective factor and a ratio of UVA to UVB attenuation. These are measures accepted or being considered by dermatologists, industry formulators and regulatory agencies worldwide. To petition FDA by their deadline of Sept .6, 2000, we embarked on a program to demonstrate conclusively that Titanium Dioxide in its different commercial variations for the personal care industry could be claimed as an effective UVA sunscreen and hence boast the claim of Broad Spectrum Sunscreen. In order to fully investigate and document our thesis we planned and carried out a multipart experiment to look at both the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of a series of formulations with Titanium Dioxide as the only active sunscreen. Then, subsequent to the FDA petition, we continued with additional variations in types of titanium dioxide coatings and mixtures we tested. Different grades of titanium dioxide were chosen to represent the full range of varieties available. These included ultra small particle, 15 nm, hydrophobically and hydrophilically coated particles, microtitanium dioxide, 35 nm particle size, both uncoated and hydrophobically coated and a larger pigmentary grade of 180 nm. To test variability in different types of formulas, both a simple oil-in-water cream and a water-in-oil silicone formulation were evaluated. Tests performed in vitro were via the Optometrics 290 SPF Analyzer utilizing IMS Vitro Skin 'rM as substrate to better mimic skin application. Clinical studies performed at AMA labs used FDA protocol for SPF and JCIA protocol for PPD assessment of UVA protection. Overall the experiments demonstrated that Titanium Dioxide could fulfill the requirements promulgated by the American Academy of Dermatology for UVA sunscreens: meet or exceed the in vitro critical wavelength of 370 nm, achieve in vivo a protective factor of four (4) as measured by PPD or UVAPF, and show some reasonable proportionality to SPF when increasing the active concentration.
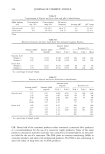
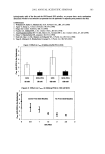
314 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Light Transmittance Curves: Comparison of Titanium Dioxide particle sizes //"• -•- 15nm .... • m 35nm _ -• m 250 nm 300 400 $oo 600 700 Wavelength (rim) As a single active ingredient titanium dioxide performed well in both UVA and UVB efficacy trials in both in vitro and in vivo assays. Further to demonstrate its versatility, higher SPF products were generated with addition of the organic sunscreen, Octinoxate, that did not sacrifice the threshold in vitro measure of 370 nm critical wavelength. Comparisons were also made versus performance of Avobenzone and Zinc Oxide, the two current contenders for UVA attenuation predominance. Commercial products with inorganic actives were evaluated in vitro with critical wavelength minimum retained for sole active Titanium dioxide products. In a wide range of formulations, Titanium Dioxide delivers benefits of broad-spectrum ultraviolet light attenuation that puts it in the short list of effective actives to reduce the premature signs of aging.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)