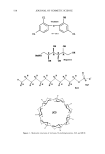
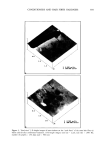
538 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE c1 Cl o• OH OH MeNH S• OH OH OH Meglumine H.- H H.- H H• H H.- H H• H H• H . ...... SLS H OH ß ! HO O OH O HO OH O . [3CD o. OH Figure 1. Molecular structures of triclosan, N-methylglucamine, SLS, and [3CD.
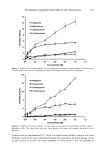
INCREASED AQUEOUS SOLUBILITY OF TRICLOSAN 539 water solubility 10 -6 g/m1-1. This lipophilic, anionic compound is compatible with many raw materials and has several dermatological uses (2). Among others, it has beneficial effects on atopic dermatitis (3,4), it reduces eczema (2) and plaque (5,6), and it can eliminate the irritant effects of sodium lauryl sulfate on the skin or buccal/lingual surfaces (6). All these applications make this antibacterial agent very useful for skin care formulations, particularly for surfactant-based hand soaps, hand disinfectants, mouth rinses, and surface cleaners (2). In two reports published in Nature, researchers showed that triclosan, far from being a generalized antimicrobial, works more like an antibiotic (7,8). Recently it was also demonstrated that triclosan kills the parasites responsible for malaria and toxoplasmosis, even at very low concentrations (9,10). Although triclosan is extensively used in cosmetic products and household chemicals, poor aqueous solubility does limit its wider application (11). Usually the poor solubility of lipophilic compounds is increased by solubilization, complexation, or salt formation (12). Savage (1) published a table listing the solubility of triclosan in commonly used solvents. To increase the solubility of triclosan, the compound has also been processed and complexed with various cyclodextrins including [3-cyclodextrin ([3CD) (11,13), •/-cyclodextrin (•/CD) (14), 2-hydropropyl-[3-cyclodextrin (HP[3CD) (15), and sulfobu- tyl ether [3-cyclodextrin (SB[3CD) (13). In all these studies the anionic triclosan/cationic SB[3CD complex increased the solu- bility of triclosan the most. Triclosan has also been converted to salts such as triclosan monophosphate to increase its solubility (16). In addition to these reports, no other detailed studies describing the enhancement of the aqueous solubility of triclosan have been found in the literature. In this study we report the effect of various additives on the solubility of triclosan in water. These solubilizing agents included ethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanol- amine, glycine, L-arginine, N-methylglucamine (meglumine), [3CD, •/CD, HP[3CD, sodium benzoate, sodium methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, and sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). In addition, the antimicrobial activity of combinations of triclosan and those solubilizers that increased its solubility was compared to the antimicrobial activity of triclosan and the solubilizing agent alone. MATERIALS AND METHODS MATERIALS Triclosan (Irgasan DP 300, Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Basel, Switzerland) was obtained from Adcock Ingram, Ltd. (Krugersdorp, South Africa). Ethanolamine, diethanolamine, triethanolamine, glycine, L-arginine, N-methylglucamine, [3CD, •/CD, sodium benzo- ate, sodium methyl 4-hydroxybenzoate, and SLS were obtained from Sigma Chemical Company (St. Louis, MO). HP[3CD was obtained from Janssen Biotech (Brussels, Bel- gium). All other solvents and chemicals were analytical grade and were used as received. SOLUBILITY MEASUREMENTS The solubility of triclosan was determined in distilled deionized water and in a 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4 (8.62 grams of sodium phosphate dibasic and 5.42 grams of sodium phosphate monobasic in one liter of Milli-Q grade water) containing increasing concentrations ranging from 0-0.2 M of [3CD, •/CD, HP[3CD, and sodium lauryl sulfate, and 0-1.0 M of sodium benzoate, ethanolamine, N-methylglucamine, D-(+)-
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)