570 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE a good styling effect on hair could be induced using submicron polymer particles (4,5). Also, according to some patents, polymer latexes having a low transition temperature deposit well onto the hair surface, finally forming a soft polymer film (6,7). In this contribution, we introduce a useful hair treatment system in which biphasic polymer latexes are used to form a nano-structured film membrane on the hair surface. The biphasic polymer latexes are synthesized by controlling the compatibility between hydrophobic components and hydrophilic components in the polymer molecule (8,9). In order to exclude the effect of surfactants, the latexes are prepared by surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. This paper then investigates the effectiveness of the biphasic polymer latex system on the film property and the deposition efficiency on the hair surface. EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS Butyl methacrylate (BMA), poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate (PEG-MA, Mw = 300, l100, 2000 g' mol-•), 2-(methacryloyloxy) ethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (METAC), and 2,2'-azobis(2-methyl propionamidine) dihydrochloride (V-50) were purchased from Aldrich Chemical Co. The inhibitor in the monomers was removed using a removing column (Aldrich). Distilled deionized (DDI) water was used through- out the process. SYNTHESIS OF BIPHASIC POLYMER LATEXES The latexes were synthesized by surfactant-free emulsion polymerization. First, V-50 (0.2 g) and DDI water (360 g) were weighed into a four-necked round flask equipped with reflux condenser, nitrogen inlet apparatus, and mechanical stirrer. Under a nitrogen atmosphere, the reactor was submerged in a thermosrated water bath and stirred with a rotation speed of 300 rpm at 75øC. After 10 min, the monomer mixture (40 g) com- posed of BMA, PEG-MA, and METAC was added to the reactor and polymerized for 10 h. The composition and designation of each sample are listed in Table I. Table I Polymerization Composition and Size Characteristics 'L Composition (wt%) Avg. Dn (nm) Symbol b BMA PEG-MA METAC DLS TEM PBMA 100 -- -- 505 453 NAS300 80 20 -- 475 386 NASl100 80 20 -- 450 347 NAS2000 80 20 -- 330 298 NAS300-M5 75 20 5 287 244 a 0.5 wt% V-50 as an initiator based on total monomer weight 10 wt% solid content. b PBMA is the abbreviation ofpoly(butyl methacrylate). In the symbolization ofNASo•-M[3, o• and [3 mean the molecular weight of PEG in PEG-MA and the concentration of METAC, respectively.
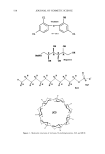
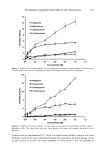
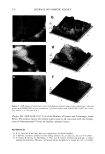
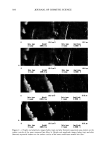
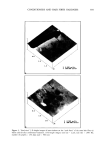
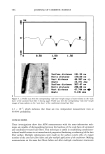
POLYMER LATEXES ON THE HAIR SURFACE 571 LATEX CHARACTERIZATIONS The particle size of the latexes synthesized was measured by dynamic light scattering (DLS, Zetasizer 3000HS, Malvern, UK). Particle morphology was observed by a trans- mission electron microscope (TEM, JEOL 2010). Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, TA Instruments, DSC 910) was used to determine the transition temperature. DSC traces were recorded from -100øC to 100øC, with a heating rate of 5øC/min under $ 2 flow. The mechanical properties of latexes were determined using an Instron uni- versal tensile testing machine at room temperature. In the DSC and Instron measure- ments, the latex film was prepared by annealing the latexes at 50øC for two days in a Teflon square molder. HAIR COATING PROCESS The applicability of the biphasic polymer latexes to hair cosmetics was evaluated by observing their degree of deposition on the hair surface. A bundle of human hairs was impregnated in the diluted latex dispersion (1 wt% polymer content, pH 6.5). After being treated for 1 min, the hairs were dried fully at room temperature. In the case of thermal treatment, the dried hairs were annealed at 80øC for 10 min. The surface characteristics of the treated hairs were then observed by a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi S-4300). The more exact topography of the treated hairs was observed again with an atomic force microscope (AFM). In the AFM measurement, a latex-treated hair was adhered onto freshly cleaved mica. The sample was observed in air by using a commercial AFM (AutoProbe LS, PSI-LS) equipped with microfabricated V-shaped silicone nitride cantilevers (force constant: 0.05 mN/m) on a scanner using the contact mode. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION CHARACTERISTICS OF BIPHASIC POLYMER LATEXES After surfactant-free emulsion polymerization, the biphasic polymer latexes obtained have a molecular structure composed of BMA, PEG-MA, and METAC units (Scheme 1). Figure 1 shows TEM images of the polymer latexes with the molecular weight of PEG in the absence of METAC. As the molecular weight of PEG increases, the latex size decreases gradually. This happens because the surface of the latexes is richly covered with PEG chains, which are responsible for the enhanced dispersion stability (8,9). Moreover, the surface activity is enhanced as a function of the length of the PEG chains (10). In ?H3 ?H3 )y C=O C=O I I o o I (CH2)3CH3 CH3 (CH2"C)z C=O I o (•H 2 CH 20)nCH 3 I•H 2 CH 2 N(CH3)3CI Scheme 1.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)