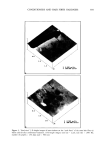
CONDITIONERS AND HAIR FIBER HARDNESS 587 • 0 0.50 1.00 1.50 Hori= Sisrance Su•oeace distance Horiz distance Uert distance Angle 182.47 nM 184.08 20.582 deg 185.24 n• 171.88 nN 55.984 18.042 deg Figure 4. Continued. eliminates errors due to fiber-to-fiber variation in pre-existing differences in microhard- ness and receptivity to conditioner deposition. The larger number of fibers investigated allows statistical comparison of the data and improves the reliability of the conclusion. This study suggests that cationic hydrophilic polymeric conditioning compounds, such as PQ-10, have a softening effect on the surface of the scale faces because of their water-retaining capabilities. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The work was carried out in context with TRI's "Analysis and Quantification of Hair Damage" project and was financially supported by a group of TRI corporate participants from the international hair care industry.
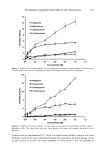
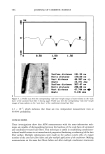
588 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 100 Depth of indent in untreated hair Mean value of indents of untreated hair (49.4 nm) Depth of indent in conditioned hair Mean value of indents of conditioned hair (61.9 nm) •= 8o ,• 60 i i i i i i i i 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 Paired Nano-indentations (#) Figure 5. Depth of nano-indentation in untreated and conditioner-treated hair. REFERENCES (1) S. B. Ruetsch, Y. K. Kamath, and H.-D. Weigmann, The role of cationic conditioning compounds in reinforcing the cuticula, J. Cosmet. Sci., 54, 63-83 (2003). (2) S. p. Chahal, N. I. Challoner, and R. T. Jones, Moisture regulation by cosmetic proteins as demon- strated by dynamic vapor sorption-•A novel efficacy testing technique, IFSCC Magazine, 3, 2 (2000). (3) Y. K. Kamath, S. B. Ruetsch, E. Petrovicova, L. Kintrup, and H.-J. Schwark, Effects of spin finish on fiber surface hardness: An investigation using atomic force microscopy and frictional measurements, J. Appl. Polymer Sci., 85, 394-441 (2002). (4) M. R. Van Landingham, S. H. Knight, G. R. Palmese, R. F. Eduljee, J. w. Gillespie, Jr., and R. L. McCullough, Relating polymer indentation behavior to elastic modulus using atomic force micros- copy, Proceedings of the Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, 440, 195-200 (1997). (5) M.R. Van Landingham, S.H. Knight, G.R. Palmese, T.A. Bogetti, R.F. Eduljee, and J. W. Gillespie, Jr., Characterization of interphase regions using atomic force microscopy, Proceedings of the Materials Research Society, Pittsburgh, 458, 313-318 (1997). (6) M. R. Van Landingham, R. R. Dagastine, R. F. Eduljee, R. L. McCullough, and J. W. Gillespie, Jr., Characterization of nanoscale property variations in polymer composite systems: Part 1: Experimental results, Compatites, Part A, 30, 75-83 (1999).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)