ALTERNATIVES TO COSMETICS PRESERVATION 111 Peeling cream. The ingrediants used in the peeling cream formulation were: water, glycerin, isopropyl myristate, Prunus dulcis amygdalus (almond) shell granules, glyceryl stearate, myristyl myristate, polyglyceryl 3-stearate, tricaprylin, stearic acid, sodium stearoyl lacty- late, cetyl alcohol, cetearyl alcohol, caprylic/capric triglyceride, Prunus dulcis amygdalus (almond) seed oil, tocopherol, xanthan gum, sodium stearate, Simmondsia chinensis (jojoba) seed oil, sodium phytate, sodium hydroxide, Chamomilla recutita (Matricaria) extract, citric acid, parfum (fragrance), limonene, and preservative system V, VI, or VII (Table III). ESSENTIAL OILS AND MULTIFUNCTIONAL INGREDIENTS WITH ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY • Planteservative WSr® (Campo Cosmetics S Pte. Ltd., Singapore) = Lonicera caprifoleum fl ower extract and Lonicera japonica fl ower extract, water. • Dermosoft GMCY® (Dr Straetmans Chemische Produkte GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) = glyceryl caprylate. • Dermosoft 688® (Dr Straetmans Chemische Produkte GmbB, Hamburg, Germany) = p-anisic acid. • Dermosoft 1388® (Dr Straetmans Chemische Produkte GmbH, Hamburg, Germany) = levulinic acid (10%), sodium hydroxide, glycerin, water. • Ethanol (not denaturated). ORGANISMS AND INOCULUM PREPARATION Organisms. Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, Escheri- chia coli, Aspergillus niger ATCC 16404, and Candida albicans ATCC 10231 were used. Inoculum preparation. For bacteria and C. albicans inoculum, the cells (108) were harvested into 0.1% peptone water by gentle agitation and adjusted to yield suspensions of approx- imately 106 cfu/ml. The count of A. niger (approx. 105) was achieved after the 1% (w/w) dilution of the initial suspension (107). The peptone water used for harvesting A. niger contained 0.05% v/v of Tween 80 (Sigma-Aldrich). MICROBIAL CHALLENGE TESTS (PRESERVATIVE EFFICACY TESTS, PETS) ACCORDING TO THE EUROPEAN PHARMACOPOEIA (E. PH.) Preliminary studies were performed in order to assure the ability of the unpreserved for- mulations to support the viability and/or microbial growth and also the effectiveness of the neutralizing medium for the inoculum recovery. The microbial challenge test was performed according to the standards proposed by the European Pharmacopoeia (E. Ph., 1996) concerning topical preparations. The formulations (samples of 20 g) were placed in sterile containers and separately inoc- ulated with bacterial and fungal suspensions to reach microbial levels of not less than 106 cfu/g for bacteria and 105cfu/g for fungi. The test samples were mixed, diluted in Letheen broth, and assayed at 0, 2, 7, 14, 21, and 28 days. The assays were performed on 1 g or 1 ml of test sample and plated in triptic soy agar and Sabouraud dextroze agar for bacteria and fungi, respectively. Plates were incubated at 35°C for bacteria and at 25°C for fungi. After a fi ve-day incubation, colonies of bacteria and fungi were counted and (cfu/g) calcu- lated. The experiments were performed in triplicate. Products are judged adequately
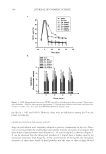
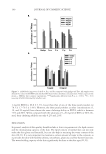
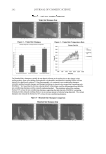
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 112 preserved when bacteria are reduced by more than 99% (2 log) after two days and more than 99.9% (3 log) after seven days yeasts and molds should be reduced by more than 99% (2 log for criterion A and 1 log for criterion B) after 14 days. MICROBIOLOGICAL QUALITY IN TWO STATES OF USE: INTACT PRODUCT AND FOLLOWING THREE WEEKS OF USE The collected samples of cosmetic products were analyzed for total aerobic plate count (S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, E. coli, A. niger, and C. albicans) in two different states of use, the intact product and after three weeks of use. One gram or 1 ml of test sample was serially diluted in Letheen broth and plated in triptic soy agar and Sabouraud dextroze agar for bacteria and fungi, respectively. Plates were incubated at 35°C for bacteria and at 25°C for fungi. After a fi ve-day incubation, colonies of bacteria and fungi were counted and (cfu/g) calculated. The experiments were performed in triplicate. In some cases A. niger was identifi ed as black colonies with the characteristic morphology of actinomycetes. RESULTS MICROBIOLOGICAL QUALITY OF THE TEST PRODUCT The results regarding the microbiological safety of the formulations tested (challenge test according E. Ph., intact products, and following three weeks of use) are summarized in Tables IV, V, VIa–e, VII and VIII and in Figures 1a–e and 2. Table IV Challenge Test Criteria Regarding Aqueous and O/W Formulations Containing Preservative Systems I-VIII Type formulation Water content (%) Water activity (aw) pH Preservative system Challenge Test criteria (E. Ph.) Physicochemical stability Tonic lotion 95 — 5.5 I B regarding A. niger and C. albicans OK — 5.5 II A No — 5.5 III A No 90 0.9 5.5 IV A OK Shampoo 74 0.932 5.5 V A OK Shower gel 65 0.893 5.5 V A OK Conditioning cream 67 0.903 5.5 V A OK Anticellulite cream 65 — 5.5 V B regarding A. niger OK 0.903 5.5 VI A OK — 5.5 VII A No Cleansing milk 65 — 5.5 V B regarding A. niger OK — VI A No 0.919 VII A OK — VIII A OK Peeling cream 47 — 5.5 V B regarding A. niger OK 0.865 5.5 VI A OK — 5.5 VII A No —Not done.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)