CLINICAL EVALUATION OF GAC EXTRACT 177 METHODS IN VITRO BIOLOGICAL TESTS DPPH radical scavenging assay. The DPPH assay was performed according to the method developed by Prior et al. (13) using solutions of 1 mM L -ascorbic acid or 1 mM Trolox to supply vitamin C or E, respectively. Ten milliliters each of Gac extract and vitamin C or E solution were mixed with 190 ml of DPPH solution. The solution was mixed by stir- ring, covered with aluminum foil and incubated in the dark for 30 min at room tem- perature. The light absorbance of the solution was measured at 515 nm using a microplate reader and the results were expressed as ascorbic acid equivalents (mg AAE/mg sample) or Trolox equivalents (mg TEAC/mg sample). 2, 2’-Azinobis 3-ethylbenzothialine-6-sulfonic acid cation radical scavenging assay. The 2, 2’-azinobis 3-ethylbenzothialine-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) scavenging assay and DPPH scavenging assay have been used to determine free radical scavenging activity (14). The method used in this study was based on that of Van den Berg et al. (15) as slightly modi- fi ed by Thaipong et al. (16) using ABTS and solutions of 1 mM L -ascorbic acid and 1 mM Trolox. Ten milliliters each of Gac extract and vitamin C or E solution were mixed with 190 mL of ABTS solution. The solution was mixed by stirring, covered with aluminum foil and incubated in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. The light absorbance of the solution at 734 nm was measured using a microplate reader and the results were ex- pressed as ascorbic acid equivalents (mg AAE/mg sample) or Trolox equivalents (mg TEAC/mg sample). Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay. The ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) assay involves the reduction of a ferric tripyridyltriazine complex to its fer- rous form to produce color in the presence of antioxidants (16). The procedure was developed by Thaipong et al. (17) using an FRAP reagent. In the assay, 300 mM acetate buffer was mixed with 20 mM ferric chloride solution and 10 mM 2,4,6-tris(2-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine (TPTZ) solution. Gac extract, vitamin C, and vitamin E was individually mixed with FRAP reagent, covered with aluminum foil, and incubated for 15 min in the dark. The light absorbance of the solution at 593 nm was measured using a microplate reader, and the results were expressed as ascorbic acid equivalents (mg AAE/mg sample) and Trolox equivalents (mg TEAC/mg sample). Tyrosinase inhibition activity. A total of 40 ml of Gac extract dissolved in 0.1 M etha- nol was added to 80 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) and 40 ml of L -dopa. A 40-ml aliquot of 0.02 mg/ml tyrosinase enzyme solution was added, and the mixture was in- cubated for 20 min. The light absorbance of the resolution was measured at 475 nm, and the percentage of inhibition activity of the tyrosinase enzymes was calculated as inhibition (%) = [(Acontrol–Bsample)/Acontrol] × 100% (18), where A is the change in the absorbance of the control sample between incubation times of 0.5 and 1.0 min and B is the change in the absorbance of the test sample after the same incubation time (19). Each result is the mean of three concurrent readings. Kojic acid was used as a positive control. Cream preparation. In this study, 5% Gac extract was incorporated into an O/W emul- sion and glycerin as excipient and continuous stirring until dispersion was complete.
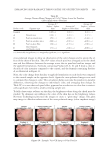
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 178 IN VIVO CLINICAL TEST Ethical considerations and declaration. This study was conducted in compliance with the ethical principles of the Offi ce of Ethics Review Committee for Research Involving Human Research Subjects, Health Science Group. The study was reviewed by the appro- priate ethics committees and approved for clinical studies. The validation number of the “Code of Approval” granted to this study is 079/2557. This study was conducted accord- ing to the ethical principles of the Helsinki Declaration (1964). Subjects. A total of 22 female subjects aged 45–61 years who had slight wrinkles or fi ne lines (crow’s feet) participated in the study. The subjects were recruited from a pool of volunteers at Dermscan Asia according to the Helsinki Declaration (1964) via a volunteer recruiter. They were instructed to systematically apply cream to the entire face twice daily. Whitening, moisturizing, and antiwrinkle measurements were obtained after 28 and 56 days of product application. Cutaneous hydration measurements. Cutaneous hydration was measured with a COURAGE & KHASAKA CM 825® Corneometer (Cologne, Germany). This instrument determines the humidity level of the most external cutaneous layers of the stratum corneum. The princi- ple of action of the Corneometer involves the modifi cation of the electrical capacities of the detector, which is designed as a condenser. The electrical capacity of the surface of the measurement tool head (which is in contact with the skin) varies according to the level of skin humidity. Changes in the dielectric constant due to skin surface hydration variations alter the capacitance of the probe. Skin color measurement. The Minolta Chroma Meter CR-321® is a colorimetric instrument that contains a xenon lamp as a light source as well as photodetectors, a microcomputer, and colored fi lters that closely match the CIE colorimetric Standard Observer curves (L*a*b* color system). The Chroma Meter converts colors perceived by humans into a digital code composed of three parameters: L*: for clarity (from dark to light) a*: for the green-to-red spectrum b*: for the blue-to-yellow spectrum a* and b* are the chrominance parameters and L* is a luminance parameter. These parameters enable close comparisons between two cutaneous zones that appear to be the same color. After the calibration phase, the measurements are performed directly on the skin using a pulsed Xenon light source as well as a dual beam system that measures the light transmitted (to correct slight deviations). Both parameters L* (luminance) and b* (cutaneous melanin yellow color) are assessed during a depig- menting product study. L* and b* are used to calculate the Individual Typological Angle (ITA°), which defi nes the skin pigmentation of a subject according to the following formula: ITA° = [Arc tan ((L*−50)/b*)] × 180/π The higher the ITA°, the lighter the skin. Thus, the higher the parameter L*, the lighter the skin the lower the parameter b*, the less yellow the skin.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)