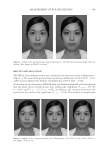
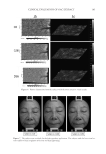
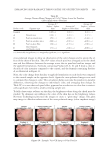
THE WHITENING AND ANTI-WRINKLE EFFECT OF PONEGRANATE 149 reader. The inhibitory activity of each sample against melanin production was calculated as follows: inhibitory activity (%) = 100-[(ODs/ODc) × 100], where ODs is the absorbance of the experimental sample at 400 nm and ODc is the absorbance of the α-melanocyte stimu- lating hormone (MSH)-treated control at 400 nm. The results are reported in terms of IC50 (the concentration at which the percentage inhibition of melanin production was 50%). MMP-1 INHIBITION ASSAY The assay was carried out using a fl uorescence microplate with modifi ed methods of Losso (25). After HDF-N cells were incubated with PCS (0.05%, 0.1%, and 1%) in the absence or presence of 312 nm UVA (5 J/cm2) for 20 min and then cultured for 24 h. The UVA source was a UV irradiation system (VILBER, Loumat, France). The average radiation intensity was approximately 3 mW/cm2. Total MMP-1 protein levels in cell culture supernatants, which includes pro, active, and inhibitor-bound MMP-1, were quantifi ed by ELISA (Human Total MMP-1 DuoSet, DY901 R&D Systems) and MMP activity using an MMP-1-specifi c activity assay (Hu- man Active MMP-1 Fluorokine E Kit F1M00 R&D Systems) according to the manufac- turer’s instructions. HISTOMORPHOMETRICAL ANALYSIS IN VIVO The histopathological profi les of each hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)-stained dorsal back skin tissues were observed under light microscope (Nikkon, Tokyo, Japan). To more de- tail changes, number of formed microfolds on the surface of epithelium (folds/mm of epithelium), mean epithelial thicknesses (μm/epithelium), and mean numbers of infl am- matory cells infi ltrated in the dermis (cells/mm2 of dermis) were calculated for general histomorphometrical analysis using a computer-assisted image analysis program (iSolu- tion FL ver 9.1, IMT i-solution Inc., Quebec, Canada) with collagen fi ber occupied regions in the dermis (%/mm2 of dermis), according to our established method (26), respectively. The histopathologist was blind to group distribution when this analysis was made. Fifty- four dorsal back skin tissue H&E-stained histological samples (three tissues in one slide three slides per group, total six groups—54 dorsal back skin tissues) were analyzed. Each group is as follows: intact control—normal nonirradiated vehicle control hairless mice UVB control—UVB-irradiated vehicle control hairless mice PCS-0.5—UVB-irradiated and PCS 0.5 ml/kg administrated hairless mice PCS-1—UVB-irradiated and PCS 1 ml/kg administrated hairless mice PCS-2—UVB-irradiated and PCS 2 ml/kg administrated hairless mice intact PCS-1—normal nonirradiated and PCS 1 ml/kg administrated hair- less mice. STATISTICAL ANALYSES All in vitro data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (S.D.) of fi ve independent experiments, and skin water content was calculated as the mean ± S.D. of eight mouse skins at each time point. Multiple comparison tests for different dose groups were conducted.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 150 Variance homogeneity was examined using the Levene test. If the Levene test indicated no signifi cant deviations from variance homogeneity, the obtained data were analyzed by one- way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a least signifi cant differences (LSD) multi- comparison test to determine which pairs in the group comparison were signifi cantly different. If the Leven test showed signifi cant deviation from variance homogeneity, a non- parametric comparison test, the Kruskal–Wallis H test, was conducted. When a signifi cant difference was observed in the Kruskal–Wallis H test, the Mann–Whitney U (MW) test was conducted to identify the specifi c pairs in the group comparison that were signifi cantly different. IC50 values for each in vitro assay were calculated by probit methods. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS for Windows (release 14.0K SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). RESULTS PCS CYTOTOXICITY To investigate the cytotoxic effects of PCS and defi ne an appropriate concentration for sub- sequent experiments, we performed WST-1 assays. Cell survival percentages were calcu- lated to determine the cytotoxic effects of various concentrations of PCS in HDF-N, HaCaT, and Melan-a cells. PCS concentrations that did not affect cell viability were selected. In HDF-N cells, concentrations ranging from 0.005% to 0.1% showed no signifi cant effect on cell numbers (Figure 1A). In HaCaT cells, no cytotoxicity was observed at concentrations ranging from 0.01% to 0.1% (Figure 1B). Concentrations between 0.005% and 0.01% showed no signifi cant reduction in cell survival in Melan-a cells (Figure 1C). MOISTURIZING BENEFITS OF PCS Moisturizing benefi ts were examined in PCS-treated HaCaT cells, which showed a signifi - cant increase in hyaluronan synthesis following treatment with 0.05%, 0.1%, and 1% PCS. Compared with vehicle-treated cells, the hyaluronan content of PCS-treated cells showed increases of 168.2%, 413.1%, and 542.6% on treatment with 0.01%, 0.05%, and 0.1% PCS, respectively. In addition, 20 mM NAG signifi cantly increased hyaluronan synthesis to 255% compared with vehicle-treated cells. Interestingly, hyaluronan synthesis induced by the addition of 0.05% and 0.1% PCS was greater than that by 20 mM NAG (Figure 2). ANTIWRINKLE BENEFITS OF PCS The effect of PCS on procollagen synthesis in HDF-N cells was evaluated using an ELISA for type I procollagen. Tumor growth factor beta (TGF-β, 10 ng/ml) altered the activity of pro- collagen by 150.9 ± 5.4%. Procollagen synthesis decreased by 96.5 ± 7.4%, 53.4 ± 8.5%, and 53.0 ± 4.4% following treatment with 0.01%, 0.05%, and 0.1% PCS, respectively. However, these changes were not signifi cant compared with control cells (Figure 3A). Elastase activity was signifi cantly inhibited by the addition of PPR (10 μM) and PCS at concentrations ranging from 0.05% to 1%. PPR (10 μM) decreased elastase activity by 74.9 ± 6% compared with vehicle-treated cells. Elastase activity increased by 92.3%,
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)