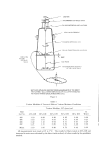
636 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 7O 6O P. ovale Counts per Field of Scurf Samples for Ten Subjects Figure 3. Average P. ovale slide counts per immersion oil objective field for all subjects DISCUSSION Except during the last 13 days of the experiment, treatment on the right side consisted of a mixture of tetracycline and nystatin, having activity against bacteria and yeasts. Results for the first 66 days sup- port the previous findings of VanderWyk (9). He had shown that elimination of the entire microbial flora from the scalp reduced scurf production in seven of nine subjects by 31%. In the present half-head experiment after a similar period a significant reduction was seen in nine of ten subjects. The average reduction for all subjects was 56.4%. The range in nine subjects was between 25.4 and 85.2%. During Period A (26 days) when the entire microbial flora on the right side was controlled by a mixture of two antibiotics, scurf reduction oc- curred in six subjects. The average reduction for ten subjects was 30%. In contrast, the left side, treated with a mixture of P. ovale suspension and tetracycline, showed an increase of 9.1% in seven subjects. The interpretation of these differences is that the yeast scalp flora (including P. ovale) plays a greater role in dandruff production than does a mixed bacterial flora. To test this idea further, treatment on the left side was changed for the next 26 days to control the yeast flora and to allow the bacterial flora to flourish. In addition, a mixed bac- terial suspension was applied to the left side. Treatment on the right side continued as before. At the end of this period, scurf production
FLORA OF THE SCALP AND DANDRUFF PRODUCTION 637 on the left side was reduced in seven of ten subjects. The average reduction was 16.8% from pre-treatment levels. On the right side scurf production continued to lessen, averaging 52.6% in all subjects. This represented an increased reduction of 22% over Period A. During Period C (14 days) treatment on the right side continued as before, but antibiotic treatment on the left side was omitted entirely. A mixture of P. ovale cells and bacteria was applied daily. The right side showed a definite leveling off in scurf production with only a 3% decrease from Period B. Previous studies (9) had shown that threshold levels were established for different individuals and that it was impos- sible to lower scurf production below certain levels by eliminating the microbial flora. A reduction was also seen on the left side (19% from Period B) despite the application of a microbial flora. Two explanations can be offered for this. The first is that the residual effect of nystatin treatment was carried over into Period C and prevented the establish- ment of a substantial yeast flora. The second is that the mixture of antibiotics applied on the right side exerted a similar suppression effect due to a possible carry over from right to left side. Microbiological studies of the scurf from both sides (Figs. 1 and 2) showed no significant increase in the microbial flora during this time. For this reason all antibiotic treatment was stopped, and a mixed microbial flora was applied to the entire scalp. After 14 days (Period D) when the experiment had to be terminated, it was apparent that scurf production was beginning to increase, particularly on the left side (Fig. 1). This period was too short to show definitely how soon scurf values would return to pre-treatment levels. VanderWyk (9) observed that under similar conditions a lag period of about 21 days passed be- fore a significant rise in scurf production was evident. Observations on Individual Subjects. Variations in results were noted among several individuals taking part in the experiment. Of the ten subjects six showed a pattern of scurf production previously described. Two subjects (4 and 8) had very low pre-treatment scurf values of 20.2 mg and 26.0 mg per sample respectively on the left side. Neither sub- ject showed any visible dandruff problem, and their scurf production did not appear to be significantly affected by antibiotic treatment. One subject (5) showed little or no change in scurf production on the right side during the first 66 days despite the continuous use of nystatin. On the left side, however, there was an increase of 95%. Microscopic studies of the scurf indicated an increase in P. ovale counts during all four treatment periods on both sides. During Period B the averaxe
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)