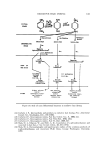
OXIDATIVE HAIR DYEING 111 concentrated p-phenylenediamine/m-aminophenol mixtures, the magenta color again develops, but the black crystalline precipitate, which forms as the reaction proceeds and which has a melting point of 237øC, does not give a magenta color on dissolution in water. Elemental analysis and the molecular weight of this product (C, 68.2 H, 5.62 N, 5.62% tool wt = 319.1433 high resolution mass spectrometer) point unequivocally to a molecular formula C•8Hx7N50. Since such a compound could be formulated as arising from the addition of a molecule of p-phenylenediamine to the 2-aminoindoaniline, we assigned the structure (XIV). This assignment is supported by the fact that acid hydrolysis gives 2.5-dihydroxybenzoquinone and p-phenylenediamine and reaction products thereof, and by consideration of the percentage con- version of p-phenylenediamine when various molar ratios of reactants are employed in its synthesis (Table II). Final confirmation is supplied by the nmr spectrum (Table III). (xiv) Table II Yields of Compound (XIV) for Various Reactant Ratios p-Diamine m-Aminophenol Temp Time Yield (M) (M) (øC) (hr) (%)• 0.01 0.01 30 24 82 0.05 0.05 30 24 93 0.05 0.05 75 5 96 0.08 0.04 40 24 91 • % of p-phenylenediamine converted. Oxidation of mixtures of 2,5-toluenediamine and m-aminophenol gave com- pounds analogous to (XIII) and (XIV). Oxidation of mixtures of p-phenylenediamine and 4-methyl-3-aminphenol (where the position para to the hydroxy group is blocked) gives rise to a ma- gena dye which could not be isolated in the pure state due to the ease with which it undergoes conversion, in concentrated solution, to a violet dye (Table IV). This latter was isolated and shown to be a 3,7-diamino-2-methyl- phenoxazinium salt (XV) by elemental analysis, its characteristic spectrum (Fig. 2) and its high pK• value of 11.2 (44,45). The magenta dye is pre- sumably 2-hydroxy-5-methylindamine (XVI). It is noteworthy that, in dilute solution, (XVI) undergoes decomposition without forming any of the phenox- azinium salt (Fig. 3) and hair dyeing experiments suggest that while the ma- genta indamine (XVI) is formed in the hair, little if any of the phenoxazinium salt (XV) is formed at the time of dyeing or subsequently.
119. JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Ox. e• (XVI) (XV) H2N / •V'"NH MeO OH (XVII) Table III The nmr Spectrum o[ Compound (XIV) in Deuterated Dimethylsulfoxide Before deuteration" After deuteration r No. of H r No. of H Assignment 2.03 1 ...... NH (quin.) 2.83 2 ...... NH.o (quin.) 4.91 4 ...... 2NH.o (benz.) 2.92 '( 2.90 • 3.08 3.04 (J: 84 cps) 3.34 4 3.26f 4 3.49 3.40 2 sets of 2 pairs of ortho H (benz.) 3.22 3.19 3.30 • 4 3.22 j• 4 (J: 90 cps) 3.45 ... 3.99 i 3.96 i lone CH • (quin.) 4.40 i 4.30 - i lone CH c (quin.) m = masked. Ortho to --NHCoH4NH.o. Ortho to --NH. Table IV Effect of Initial Hydroxyindamine (XVI) a Concentration on the Yield of the Phenoxazime (XV) Concn (M) 10 -• 2.5 X 10 -• 5 X 10-'* 10 -'ø 10-' Yield, % 0 • 2.6 • 5.7 b 11.4 • (O" Formed by reaction of 1 molar proportion of each of p-phenylenediamine and 3-amino- 4-methylphenol and 6 molar proportions of potassium ferricyanide, at room temperature followed by 2 hr at 98 ø C. Determined spectrophotometrically. Determined gravimetrically.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)