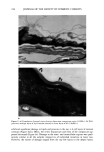
248 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Figure 3. Image representing the echographic aspect of the skin of the volar forearm after application of petrolatum. The epidermis echo and the echogenicity of the lower dermis have clearly decreased in com- parison to normal skin. Table III Superficial 201-255 Pixels at Skin Sites Treated With Petrolatum and Two Commercial Products Petrolatum Moisturizer 1 Moisturizer 2 Baseline 352.73 + 223.92 368.33 + 227.48 428.4 + 183.74 Removal 183.87' + 67.78 167.33' _+ 62.23 191.13' _+ 82.56 15 min 252.47* + 103.86 181.73' _+ 62.81 222.8* + 95.76 30 min 220.67* _+ 75.52 168.33' + 49.85 231.2' + 93.5 60 min 221.33' + 74.72 206.53* + 102.02 258.4* + 113.82 120 min 201.8' + 86.25 208.53* _+ 106.19 232.33* _+ 99.83 180 min 207.47* _+ 80.91 217.73' + 72.6 267.13' + 88.06 * Significant in respect to baseline.
20 MHz B-SCANNING 249 201-255 pixels 900 800 - 700 - 600 - 500 - 400 - 300 - 200 - IO0 baseline rem 15' 30' 1 h 2h 3h • petrolatum • moisturizer 1 • moisturizer2 Figure 4. Image analysis on echographic pictures. Variation of the extension of areas reflecting within the 201-255 interval in the lower dermis. *Significant in respect to baseline values. corneum by two different mechanisms, the first by delivering their water to the skin, and the second by occlusion (9). In fact, it has been demonstrated that lipids contained in petrolatum penetrate to all levels of the stratum corneum, replacing intercellular bilayers, supporting the concept that petrolatum and other moisturizers do not simply form an inert, epicutaneus, oc- clusive membrane, but actively contribute to the hydration process and barrier recovery (15). In our study, too, after removal of the moisturizers, TEWL was higher, owing to evaporation of the water included in the test substances that penetrated into the stratum corneum during the application period. At the same time, capacitance values rose both for the two test formulations and for petrolatum. Contrary to the findings of Marti- Mestres et al. (16), we did not observe a decrease in TEWL after application of petro- latum. Instead, a slight increase in TEWL was assessable even at petrolatum test areas. This different observation may be due to the different experimental procedure employed by these authors, whereby the residues of petrolatum, forming an occlusive membrane, were not removed from the skin before performing measurements. Echographically, dermal modifications induced by topically applied substances causing edema or inflammation are appreciated as an increase in the extension of hypo-refiecting areas (17-20). Occlusion exerted by an empty Finn-Chamber on the skin induces a slight edema that is assessable by ultrasound (21). In this study, image analysis on echographic
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)