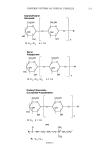
230 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Ni-filtered Cu-K o• radiation (1.542 A), a voltage of 40 kV, a current of 40 mA, and a goniometer angular increment of lø/min. STABILITY STUDIES To evaluate temperature stability, aqueous 1,3-butylene glycol solution was prepared and divided into two parts. LG106W in free or complex form was added to each solution. The solutions were moved to 5.0-ml Teflon (FEP) centrifuge tubes (Nalgene, Nalge Company, New York). The tubes were sealed with parafilm and kept at 25øC, 40øC, and 50øC in temperature-controlled chambers. Periodically, 0.1-ml aliquots of these were pipetted out and then diluted with 50% v/v methanol. The solutions were analyzed for LG106W by HPLC. In the case of the pH stability study, a universal buffer solution was prepared and the experiment was conducted under the same conditions as those of the temperature test. INHIBITION OF MELANIN SYNTHESIS AND CYTOTOXICITY B16 mouse melanoma cells were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum in a humidified incubator at 37øC under 5% CO 2. The cells were seeded into a 6.0-cm petri dish at a density of 5 x 105 cells per dish. After the cells were attached, the medium was replaced with fresh medium containing various concentrations of LG106W and its CyD inclusion complexes. The cells were cultured for two days, and the medium was replaced with fresh medium once more, further incubated for a day. Then the cells were harvested with a cell scraper (10). The inhibition of melanin synthesis was evaluated by an expert's sight. In order to screen the potential toxicity of raw materials, an MTT (3-[4,5- Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide thiazoyl blue) reduction test was carried out. First, V79-4 cells (Chinese hamster, continuous cell line of lung tissue fibroblast) were cultured, and then the serial dilutions of the test materials were applied to the cultured cells for 24 hr. For a viability check, the MTT test was performed according to the method described previously (11). MTT-formazan extracts were mea- sured by reading the absorbance at 570 nm. IN VITRO SKIN PERMEATION The skin permeability of LG106W was determined in vitro. Female hairless mice (8- week-old) were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and their full-thickness skins were removed and placed on Franz-type diffusion cells with an effective diffusion area of 1.766 cm 2 and a receptor volume of 7.0 ml (Microette, Hanson Research Co., CA). The receptor compartment consisted of isotonic aqueous 50-mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) containing 1.0% w/v HP-IB-CyD. The receptor compartment was kept at 32øC by circulating water through an external jacket and stirring with a magnetic bar. The vehicle compositions of the donor compartment selected for the incorporation of LG106W and of the inclusion complex were of two types: water and an oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion base. The formula of the emulsion was selected for its viscosity, spread- ability, and stability. The following was adopted: cetostearyl alcohol 0.5% w/w glyceryl
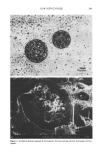
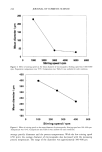
LG106W AND INCLUSION COMPLEXES 231 monostearate 0.5% w/w PEG100 stearate 0.5 % w/w mineral oil 15.0% w/w PEG40 stearate 1.0% w/w sorbitan stearate 0.5% w/w glycerine 10.0% w/w carbomer 0.1% w/w and water 71.9% w/w. The emulsion and water vehicle contained 0.5% of LG106W, or the equivalent amount of the material in the form of an inclusion complex. One milliliter of the donor compartment was applied to the skin surface and 0.7-ml aliquots were withdrawn from the receptor compartment at predetermined times and replaced with an equal volume of fresh buffer solution maintained at 32øC. The samples were analyzed for LG106W by HPLC. Each experiment was repeated at least three times, and the results reported are the mean values + standard error of the mean (SE). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION PHYSICOCHEMICAL ANALYSIS OF INCLUSION COMPLEXATIONS Analysis by scanning electron microscope (Figure 2) revealed the crystallization of [3-CyD in polyhedral form with relatively large dimensions (Figure 2B), whereas LG106W was substantially in needle shape (Figure 2A). The inclusion complex obtained by precipitation occurred in the form of large freestanding or overlapping hexagons, and it had a relatively smooth surface. This observation, while revealing a clear difference Figure 2. Scanning electron microscopy of LG106W (A), [•-CyD (B), LG106W-I•-CyD complex precipi- tate (C), and physical mixture (D).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)