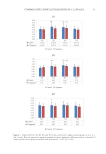
8 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE RESULTS Forty-four subjects were randomized into control and test groups. There were no significant differences in age, skin phototypes and skin type between the two groups. Baseline characteristics are shown in Table I. SKIN LIGHTENING EFFECT The skin lightening effect of C lappacea cream was evaluated by measuring a decrease in the mean MI after 4 weeks of product application. The results are shown in Figure 2. There was no significant difference in mean MI between the control and treatment groups at baseline. As shown in Figure 2a, both the control and treatment groups showed significant pigment reduction in melasma sites after 4 weeks of treatment. The lightening effect was significant even by the second week of treatment (p 0.01). The C lappacea product caused steady pigment reduction throughout the 4 weeks of treatment, and its effect was still observable after the treatment finished (week 5). The control product resulted in decreased MI at week 2, which then increased by week 4 before decreasing again to week 5. Overall, the mean and percentage reduction in MI from baseline to week 4 were significantly higher in subjects who used the C lappacea product relative to controls (–36.5 AU, 12% versus –13.73 AU, 4.68% p 0.05). Pigment reduction in normal skin exhibited a similar trend as in the melasma area (Figure 2b). There were significant decreases in mean MI by the second and fourth weeks of treatment in both the treatment and control groups. The mean and percentage reduction in MI by the fourth week were higher in the C lappacea group than the control, but this difference was not statistically significant (–37.09 AU, 14.6% versus –20.59 AU, 7.9%). One subject (4.5%) in the C lappacea treatment group had a higher MI after the treatment. In contrast, 7 subjects (32%) in the control group had a higher MI. EFFECT ON SKIN BIOMECHANICAL PROPERTIES Changes in the R parameters during and after the treatment are shown in Figure 3. There were no significant differences in any R parameters between the treatment and control groups at baseline. Table I Baseline Characteristics of Control and C lappacea Groups Control group (n=22) C lappacea group (n=22) Age, y, mean ± SD 45.22 (±6.68) 46.62 (±6.12) Age min–max (y) 30–54 33–55 Skin phototypes, n (%) III 3 (13.6) 7 (31.8) IV 8 (36.4) 9 (41) V 11 (50) 6 (27.2) Skin type, n (%) Oily 2 (9.1) 4 (18.2) Combination 13 (59.1) 10 (45.5) Normal 6 (27.3) 7 (31.8) Dry 1 (4.5) 1 (4.5)
9 COMPARATIVE CLINICAL EVALUATION OF C LAPPACEA SKIN FIRMNESS AND SKIN RESILIENCE There was a statistically significant (p 0.01) decrease in R0 after 4 weeks of application in both the treatment and control groups, suggesting an improvement in skin firmness. However, there was no significant difference in the results between the C lappacea cream and the control product. R1 decreased significantly (p 0.05) in the C lappacea group but did not change significantly in the control group. This finding suggests that the C lappacea product was better than the control at returning the skin to its original state and thus at improving skin resilience. Figure 2. Mean MI at melasma (2a) and on normal skin (2b) between the control and treatment groups at 0, 2, 4, and 5 weeks (1 week after stopping treatment). Data are reported as mean ± standard deviation. Significant differences relative to baseline (week 0) and the control group are marked with asterisks (*p 0.05, **p 0.01).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)