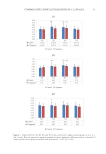
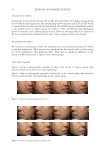
12 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE SKIN ELASTICITY EFFECT Continuous increases in the mean R2, R5, and R7 were observed in the C lappacea group during the 4 weeks of cream application. The control group showed increases in R2, R5, and R7 by the second week but then decreased by the fourth week. R2 and R5 increased significantly relative to the baseline in the C lappacea group (p 0.05, p 0.01), and R5 increased significantly relative to baseline in the control group (p 0.01). However, the magnitude of the increase in R5 was not significantly different between the C lappacea group and the control group. SKIN HYDRATING EFFECT R6 increased continuously in both the treatment and control groups during the 4 weeks of product application. This increase was significant by the fourth week in both groups (p 0.01), confirming a skin hydrating effect. There was no significant difference in the increase of R6 between the C lappacea and control groups. VISIA® PHOTOGRAPHS Figure 4 shows a photographic example of subject #43 in the C lappacea group, who presented the best result for skin color lightening. Figure 5 shows a photographic example of subject #5 in the control group, who presented the best result for skin color lightening in the control group. Figure 4. Times-series photographs of subject #43. Figure 5. Time-series photographs of subject #5.
13 COMPARATIVE CLINICAL EVALUATION OF C LAPPACEA SAFETY MONITORING All subjects completed the study, with 9% of subjects (2/22) from the C lappacea group and 22% (5/22) from the control group reporting some degree of intolerance during their first use of the products. However, the intolerance was mild and disappeared spontaneously without recurrence by the second application. No rashes, skin redness, exfoliation, or increased acne were observed during the product application period. SUBJECT SATISFACTION All subjects completed a satisfaction questionnaire. 100% of subjects in the C lappacea group and 95% of subjects in the control group appreciated the organoleptic characteristics and efficacy of the treatment. In addition, all subjects reported that they would like to continue using the product and will recommend the product to a friend. 91% of C lappacea subjects and 100% of control subjects were willing to purchase the cream at the end of the study. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This is the first clinical study to demonstrate the efficacy and tolerability of a new facial cream formulated using C lappacea extract. Objective measurements taken with a Mexameter® (Courage + Khazaka Electronic GMBH, Köln, Germany) demonstrated that the C lappacea extract cream provided significantly better skin lightening effects than the control cream after 4 weeks of use. In addition, C lappacea extract cream had significant skin lightening effects on both melasma and normal skin relative to baseline. The extent of skin lightening was satisfactory and was clinically evident in some subjects. Based on Mexameter® (Courage + Khazaka Electronic GMBH, Köln, Germany) results from other studies (12,13), the skin lightening effects of C lappacea extract cream could be observed much earlier than the effects of standard skin lightening agents such as hydroquinone. The clinical response to 2–5% hydroquinone becomes evident only after 5–7 weeks, and therapy may be continued for 3–12 months (14). The skin lightening effects of C lappacea extract cream could be related to the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and tyrosinase inhibition properties of C lappacea (3,4). Based on the steps of melanogenesis, there are three potential mechanisms of action for natural and chemical skin lightening agents: (1) regulation of melanin synthesis, (2) interference with melanosome maturation and transfer, and (3) transepidermal melanin elimination (15). Many flavonoids plant extracts regulate melanogenesis by directly inhibiting tyrosinase or acting on the other parts of melanin synthesis pathway (15–17). Antioxidant and anti- inflammatory activities of these natural plants can also affect the melanin regulation pathway (15). Moreover, anti-inflammatory activity would theoretically help decrease skin redness following an inflammatory mechanism. In this study, the C lappacea extract cream caused steady pigment reduction throughout the 4 weeks of treatment, whereas subjects using the control cream showed worsening of pigmentation by the end of treatment. Several studies have reported the worsening of pigmentation as a side effect of melasma treatment, mostly in individuals with darker skin color and high sun exposure (14,18–20). Using a high concentration of topical lightening
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)