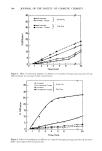
NITRITE ASSAY METHOD 389 from day to day. The cause of turbidity in final solutions was suspected to be due to the sample carried into the aqueous layer by the small amount of chloroform dissolved in the aqueous layer. Slow loss of the dissolved chloroform in aqueous layer, during the color development steps of the assay, appeared to separate the water-insoluble sample out of the solution. Filtration of centrifuged aqueous extracts of the samples through Whatman //42 filters prior to the color development was found to solve turbidity problems. The filtration step was incorporated into the final sample preparation procedures (Procedure A and Procedure B) described in the Experimental Section. This filtration step also acts as a safeguard against turbidity interferences due to factors other than the one described above. PRECISION AND ACCURACY The precision and accuracy of the method utilizing Procedure A for sample preparation was determined by analyzing propylene glycol samples spiked with sodium nitrite. The amount of nitrite spiked was calculated so that the nitrite nitrogen content of propylene glycol would be in the range of 0.677 to 1.015 mg/kg. The results are summarized in Table II. Similarly the precision and accuracy of the method using Table II Precision and Accuracy Data for the Nitrite Assay Method using Sample Preparation Procedure A Sample Propylene GlycoP Nitrite Nitrogen 2 Absorbance 3 Nitrite Nitrogen Percentage of g spiked,/xg (543 nm) found,/xg Absolute Recovery 1.002 -- 0.0036 -- 1.002 -- 0.0073 -- 1.002 -- 0.0058 -- 0.802 1.058 0.0781 1.044 1.002 1.058 0.0772 1.022 1.002 1.058 0.0766 1.045 1.002 1.058 0.0782 1.062 1.202 1.058 0.0794 1.031 -- 1.058 (Standard) 0.0738 -- 1.058 (Standard) 0.0733 Average Percentage of Absolute Recovery, X 99.0 (n = 5) Relative Standard Deviation, RSD 1.55 95% Tolerance Limits 4.30 100.3 96.6 98.8 100.4 98.9 •Added as 8.0, 10.0 or 12.0 ml aliquot of a stock solution containing 10.02 g/100 ml. 2Added as a 5.0-ml aliquot of a freshly made nitrite solution containing 105.8/xg nitrite nitrogen/500 mi. 3The absorbance is due to the total nitrite, spiked as well as the nitrite present in propylene glycol as an impurity. A correction for the contribution by nitrite impurity is made in calculating the Nitrite Nitrogen found and the Percentage of Absolute Recovery. sample preparation, Procedure B, were determined by analyzing stearic acid samples spiked with sodium nitrite. The results are summarized in Table III. Since propylene glycol and stearic acid also contained nitrite in addition to the spiked nitrite, it made a contribution to the absorbance of spiked samples. In calculating the percentage of absolute recovery values, the absorbance values of spiked samples were corrected by subtracting the absorbance due to unspiked samples of propylene glycol or stearic acid.
390 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table III Precision and Accuracy Data for the Nitrite Assay Method using Sample Preparation Procedure B Sample Stearic Acid • Nitrite Nitrogen 2 Absorbance 3 Nitrite Nitrogen Percentage of spiked, 3tg (543 nm) found, 3tg Absolute Recovery 1.034 -- 0.0080 -- 1.034 -- 0.0089 -- 0.776 0.846 0.0664 0.860 1.034 0.846 0.0678 0.850 !.034 0.846 0.0646 0.804 1.034 0.846 0.0682 0.856 1.292 0.846 0.0677 0.813 -- 0.846 (Standard) 0.0585 0.846 (Standard) 0.0595 -- Average Percentage of Absolute Recovery, X 98.9 (n = 5) Relative Standard Deviation, RSD 3.12 95% Tolerance Limits 8.65 101.7 100.5 95.1 101.2 96.1 •Added as 15.0, 20.0 or 25.0 ml aliquot of stearic acid stock solution in chloroform, containing 10.34 g/200 mi. 2Added as 50.0 ml aliquot of freshly made aqueous nitrite solution containing 8.46 3tg nitrite nitrogen/500 mi. 3The absorbance is due to the total nitrite, spiked as well as the nitrite present in stearic acid as an impurity. A correction for the contribution by impurity is made in calculating the Nitrite Nitrogen found and the Percentage of Absolute Recovery. It is evident from the data in Tables II and III that the assay method using either of the sample preparation schemes (A or B) has good precision and accuracy, as shown by the relative standard deviation and percentage of absolute recovery values, respectively. APPLICATION OF METHOD The nitrite assay method described herein was applied to a number of raw materials commonly used in pharmaceutical/cosmetic creams and lotions. Over 80% of the raw Table IV Applicability of Nitrite Assay Method to Raw Materials Procedure A Procedure B Acetamide MEA Bees wax Alcohol BHA Aluminum chlorohydrate Cetyl alcohol Amphoteric-2 Fragrances Animal protein derivative Glyceryl stearate Citric acid Isopropyl myristate Disodium EDTA Lanolin alcohol Glycerin Lanolin oil Laureth-4 Methyl & propyl parabens Poloxamer-184 & 188 Mineral oil Propylene glycol PEG-8 Sodium chloride PEG-4 dilaurate Sodium decylbenzenesulfonate PEG-40 stearate Sodium phosphate Petrolatum Sorbitol PPG-15 stearyl ether Sorbitan sesquioleate Sorbic acid Stearic acid
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)