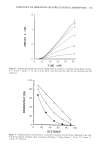
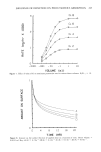
HPLC-TEA ANALYSIS OF NDELA 215 The average response factor was employed to determine the level of NDELA present in each of the samples analyzed. Sample analysis. As discussed below, the final procedure was as follows: 1. Quantitatively add -5 ng/injection (e.g., 100 •tL of 500 ng/mL) of NPYR in chromatographic solvent and dilute the sample to a known volume (e.g., 5 ml). 2. Inject a known volume (50-75 •1) of each sample onto a Spherisorb CN column (Laboratory Data Control) with a Series B- 110, 0 to 100 •1 syringe (Applied Science Laboratory, State College, Penn.). 3. Monitor the UV response at 0.1 to 0.5 absorbance units full scale and the TEA response at an attenuation of X 2. 4. Before each sample injection analyze a reference solution of NDELA to ensure reproducible TEA response. When possible, select a reference solution which cor- responds to the estimated level of NDELA in the next sample. Method of calculation. The level of NDELA in a sample was calculated from the TEA peak height (PH) response to NDELA in the sample and in reference solutions by the following simple rearrangement of the RWR equation, PH NDELA wt NPYR wt NDELA/aliquot = X PH NPYR RWR Table I HPLC Parameter Evaluation for NDELA Determination (Spherisorb Silica, 5 •m) Flow NDELA a Eluent Rate k' PAF b W0.1 c (min) 50/45/5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/45/5 Hexane/methylene chloride/methanol 75/22.5/2.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/49/1 Isopropanol/hexane/methanol 75/24.5/0.5 Isopropanol/hexane/methanol 75/25 Isopropanol/isooctane 50/50 Isopropanol/isooctane 73.5/25/1.5 Methylene chloride/isopropanol/ acetonitrile 75/25 Methylene chloride/isopropanol 50/50 Hexane/isopropanol 80/16/4 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 65/31.5/3.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/47.5/2.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 65/33.25/1.75 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 75/20/5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 60/30/10 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 75/19/6 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 3.0 0.9 1.2 0.5 2.0 •0 1.3 1.4 3.0 1.7 3.5 1.1 2.0 1.0 4.3 1.5 2.0 1.0 2.5 1.1 2.0 1.0 4.5 1.3 2.0 •0 5.0 1.9 2.0 •0 4.4 1.7 2.0 --0 4.3 1.5 2.0 •0 5.7 3.9 1.0 2.3 1.3 1.2 1.0 1.0 3.0 1.7 1.0 0.9 1.8 1.2 2.0 1.1 1.7 0.7 1.0 1.3 1.8 1.1 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.6 1.0 2.0 1.6 1.0 1.5 1.5 0.6 0.5 1.5 3.3 0.7 0.7 elution volume NDELA--void volume a k' = void volume width of back half of peak at 10% height b PAF = peak asymmetry factor = width of front half of peak at 10% height c W0 • = width of peak at 10% height.
216 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II HPLC Parameter Evaluation for NDELA Determination (•Bondapak CN Column) Eluent Flow NDELA a Rate k' PAF b W0,1 t (min) 75/20/5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/40/10 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 90/8/2 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 82/14.4/3.6 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 60/34/4 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 65/26.25/8.75 Isooctane/methytene chloride/ methanol 75/19/6 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 3.0 1.0 1.0 0.6 2.0 1.2 0.7 0.7 1.0 1.0 1.2 0.9 1.0 1.5 0.6 1.3 2.0 5.0 2.3 1.7 2.0 1.6 0.8 0.9 1.0 1.0 1.1 1.1 1.0 1.8 1.8 1.2 1.0 1.0 1.3 1.0 3.0 3.1 0.8 0.6 1.5 2.3 1.5 1.0 1.0 2.3 1.8 1.3 elution volume NDELA--void volume void volume width of back half of peak at 10% height b PAF = peak asymmetry factor = width of front half of peak at 10% height c Wo. 1 = width of peak at 10% height. NDELA confirmation. For those samples with quantifiable levels of NDELA, the HPLC- TEA NDELA peak was confirmed as a nitrosamine by transferring an aliquot of the sample solution to a culture tube and irradiating it with a UV lamp (Hanovia Utility Ultraviolet Quartz Lamp, Engelhard Hanovia, Inc., Newark, N.Y.) at a maximum wavelength of 360 nm. An aliquot of the irradiated sample was reanalyzed by HPLC- TEA and the reduction in the HPLC-TEA NDELA peak measured. After 30 rain of irradiation, approximately 90% reduction in the NDELA peak could be expected. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Since water is incompatible with the TEA detector, only nonaqueous HPLC systems were investigated. Three columns were evaluated with a variety of eluents: Spherisorb Silica (5 •tm), •tBondapak CN, and Spherisorb CN (5 p•m). As can be seen from Tables I and II, which give HPLC parameter evaluations by column, the nitrile column (•Bondapak CN) gave superior chromatography for most of the test solvent systems. Using the nitrile column, the 75/19/6 isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol eluent gave the largest k' with good peak shape. Subsequent investigations found that the Spherisorb CN, 5 •m column gave superior resolution compared to that of the }xBondapak CN column, and the former column was specified as the column of choice for most applications. The sample workup procedure affects the choice of chromatographic conditions to some extent. If the sample extract is dissolved in a nonpolar solvent such as hexane, a silica column would be preferable, while the nitrile column would be more appropriate for a sample dissolved in ethyl acetate or other polar solvent.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)