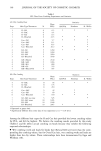
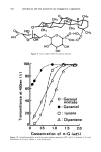
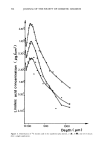
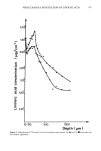
HAIR BLEACHING AND WAVING 169 1.Dimension - Separation Parameter. Charge af pH 3 -1.1 -1.2 6 a BLEACHED oerom • s•mpl½ ooe bleached oeu•op½•n brown h•i• (Bindcw•ld
170 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS The mechanism of the reduction follows a two step equilibrium as shown in the fol- lowing equations: K - S - S - K + R - SH -- K - S - S - R + K - SH K - S - S - R + R - SH -• R - S - S - R + K - SH K - S - S - K + 2R - SHoR - S - S - R 4- 2K - SH R - SH = Thioglycollic acid K - S - S - K = Cystine in keratin Studies by Gumprecht et al. (21) found 17-43% of cystine being reduced during the usual treatment time of twenty minutes. Strtil3mann (22) at DWI obtained generally similar results. On European brown hair, degrees of reduction of 16-22% were esti- mated by S-carboxymethylation of the thiol groups formed during waving treatment. The S-carboxymethylcysteine determined by amino acid analysis represents the extent of cystine being reduced. A schematic diagram of the procedure is given in Figure 8. R-S -S-R [OHBINED [YSTINE IN HAIR 1. HSEH2EOOH NH6OH 2. DIALYSIS pH 3.0 3 IEH2EOOH {pH 8.9,3h} 2R- COMBINED S EH2EOOH S-EARBOXYMETHYLEYSTEINE IN HAIR •7 1. TOTAL HYDROLYSIS 2. AHINO ACID ANALYSIS HOOE - EH (NH2)EH2 - S- CHzEOOH FREE S-EARBOXYMETHYLEYSTEINE Figure 8. Schematic diagram of procedure for the determination of the degree of reduction during perma- nent waving investigations.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)