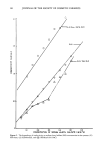
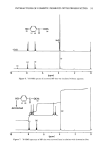
CONDUCTIVITY OF SKIN IN DETERGENT SOLUTIONS 71 EFFECT OF PHARMACOPEIA CREAMS AND OINTMENTS ON SKIN RESISTANCE The application of cream or ointment films on the skin surface increases skin resistance (Figure 4). The extent of increase in normalized resistance and the duration of mainte- nance of high resistance were found to depend on the type of ointment formulation used. The results suggest that the degree of barrier efficiency can be ranked in the following order: white petrolatum hydrophilic petrolatum hydrophilic ointment •PEG ointment. Apparently, white petrolatum behaved as a mechanical barrier. The effect lasted for more than six hours. On the other hand, PEG and hydrophilic oint- ments, which are water-soluble and water-washable in nature, showed poor retention of skin resistance due to their hydrophilic characteristics and were thus easily washed off the skin. 200• 100• I 01NTM E NT V CREAM c 0 12 24 36 48 60 Time(mir,) Figure 5. Skin resistance after treatment with commercial barrier creams. 0.5% SLS solution was present in the donor compartment. (0) ointment V, (•) cream N, (I,) cream D, (I)cream C, and (I) cream P.
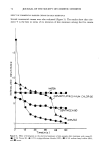
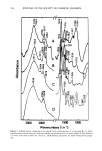
72 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS EFFECT OF COMMERCIAL BARRIER CREAMS ON SKIN RESISTANCE Several commercial creams were also evaluated (Figure 5). The results show that oint- ment V is the best in terms of its retention of skin resistance among the five creams WATE• Q5%C.r..'-TYLPYR• D• N IUM CHLORIDE 5 'l'irne(rni n ) EN80 0.5%S• Figure 6. Effect of detergents on the electrical resistance of skin samples after treatment with cream D. (,) 0.5% Tween 80, (&) 0.5% cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC), (O) 0.5% sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), and (I) water.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)