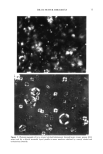
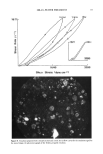
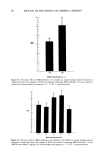
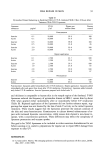
64 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Regarding true hydration of the skin, our model lipid predicts that glycerol, present at 5- 15% of the intercellular lipid, will reduce water loss and that 15% adds water to the skin, from the atmosphere, when the skin is exposed to high humidity. The model predicts that glycerol will have no effect on the water content of skin exposed to low humidity but that glycerol will act as a skin conditioner, maintaining the pliability of the tissue. It is difficult to make the comparison between these in vitro results and in vivo studies of skin hydration by glycerol because the latter studies do not measure water content per se. Rather, one infers this from transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements. There have been conflicting opinions as to the significance of TEWL values. It was originally believed that moisturizing agents occlude the skin and reduce TEWL. How- ever, more recent evidence indicates that increased skin hydration parallels increased water flux (24,25). Thus, a true "moisturizer" may cause an increase in TEWL. In the case of glycerol, these trends are dependent on the environment. It has been found that the addition of glycerol reduces TEWL of skin under high humidity (65% RH) (16). On the other hand, when glycerol is added to skin in vivo at low humidity, TEWL values increase (12,14), persumably due to the attraction of water from the lower epidermal layers into the stratum corneum, where it then evaporates. Glycerol thus acts as a conduit for water loss under dry atmospheric conditions. This effect probably accounts for the visible improvement in skin by glycerol under dry conditions. Unfortunately, our low hu- midity data cannot be compared with these in vivo findings because our model does not include a hydrated reservoir beneath the stratum corneum lipid. This is a shortcoming of the model and must be borne in mind when comparing our experimental results with those of in vivo studies. In total, the model lipid appears promising as a predictive tool for studies of skin moisturization/conditioning. REFERENCES (1) S. E. Friberg and D. W. Osborne, Samll angle x-ray diffraction patterns of stratum corneum and a model structure for its lipids, J. Disp. Sd. and Technol. 6, 485-495 (1985). (2) A.M. Kligman, in The Epidermis, W. Montagna, Ed. (Academic Press, New York, London, 1964). (3) G. Imokawa and M. Hattori, A possible function of structural lipids in the water-holding properties of the stratum corneum, J. Invest. Dermatol., 84, 282-284 (1985). (4) C. Prottey, P.J. Hartop, J. G. Black, and J. I. McCormack, The repair of impaired epidermal barrier function in rats by the cutaneous application of linoleic acid, Br. J. Dermatol., 94, 13-21 (1976). (5) P.M. Elias, B. E. Brown, P. Fritsch, J. Goerke, G. M. Gray, and R. J. White, Localization and composition of lipids in neonatal mouse stratum granulosum and stratum corneum, J. Invest. Der- matol., 73, 339-348 (1979). (6) P.M. Elias, Lipids and the epidermal permeability barrier, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 270, 95-117 (1981). (7) S. E. Friberg, I. Kayali, and L. Rhein, Direct role of linoleic acid in barrier function: Difference between linoleic and oleic acid, J. Disp. Sci. and Technol. (in press). (8) K. Laden, The role of glycerol in skin hydration, J. $oc. Cosmet. Chem., 13, 455-458 (1962). (9) D. R. Highley, V. O. Savoyka, J. J. O'Neill, and J. B. Ward, A stereomicroscopic method for the determination of moisturizing efficacy in humans,J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 27, 351-363 (1976). (10) M. A. Lampe, A. L. Burlingame, J. A. Whitney, M. L. Williams, B. E. Brown, E. Roitman, and P. M. Elias, Human stratum corneum lipids: Characterization and regional variations, J. Lipid Res., 24, 120-130 (1983).
GLYCEROL EFFECT ON STRATUM CORNEUM LIPID 65 (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) (19) (20) (21) (22) (23) (24) (25) (26) L. E. Gaul and G. B. Underwood, Relation of dew point and barometric pressure to chapping of normal skin, J. Invest Dermatol., 19, 9-19 (1952). M. M. Rieger and D. E. Deem, Skin moisturizers. II. The effects of cosmetic ingredients on human stratum corneum,J. Soc. Cosmet., Chem., 25, 253-262 (1974). W. P. Smith, M. S. Christensen, S. Nacht, and E. H. Gans, Effect of lipids on the aggregation and permeability of human stratum corneum, J. Invest. Dermatol., 78, 7-11 (1982). I. M. Lieb, R. A. Nash, J. R. Matias, and N. Orentreich, A new in vitro method for transepidermal water loss: A possible method for moisturizer evaluation, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 39, 107-119 (1988). D. W. Larsen, S. B. Rananavare, F. E. Stary, M. E1 Nokali, and S. E. Friberg, Molecular motion and phases in an equimolar phosphatidylcholine/ethylene glycol system, J. Phys. Chem., 88, 4015-4018 (1984). D. L. Bissett and J. F. McBride, Skin conditioning with glycerol, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 35, 345-350 (1984). M.D. Batt and E. Fairhurst, Hydration of the stratum corneum, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 8, 253-264 (1986). M.D. Batt, W. B. Davis, E. Fairhurst, W. A. Gerrard, and B. D. Ridge, Changes in the physical properties of the stratum corneum following treatment with glycerol, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 39, 367-381 (1988). D. W. Osborne, The skin softening properties of maleated soybean oil, Cosmet. Toiletr., 103, 57-70 (1988). M. Takahashi, Y. Machida, and Y. Tsuda, The influence of hydroxy acids on the rheological proper- ties of stratum corneum, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 36, 177-187 (1985). K. J. Hall and J. C. Hill, The skin plasticization effect of 2-hydroxyoctanoic acid. 1: The use of potentiators,J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 37, 397-407 (1986). J. C. Hill, R. H. White, M.D. Barratt, and E. Mignini, The skin plasticization effect of a medium chain 2-hydroxy acid and the use of potentiators, J. Appl. Cosmetol., 6, 53-68 (1988). S. Fleischer and M. Kervina, Long-term preservation of liver for subcellular fractionation, Methods Enzymol., 31, 3-5 (1974). R. O. Potts, Stratum corneum hydration: Experimental techniques and interpretation of results, J. Soc. Cosmet. ½hem., 37, 9-33 (1986). R. L. Rietschel, A method to investigate skin moisturizers in vivo, J. Invest. Dermatol., 70, 152-155 (1978). S. E. Friberg, I. Kayali, L. Rhein, and R. Hill, A model for the stratum corneum lipids and some implications, Cosmet. Toilet., 102, 135-139 (1987).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)