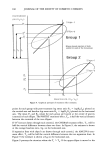
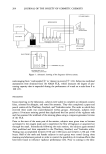
186 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS PostTreatment LOG ( R 'C1. -a .•••Slope = 1 /..--$'"1"6"p e = b Group 1 Ellipses denote clusters of d•ta points for each of the tt•o õroup$ Group 2 51ope=l ...2 Baseline LOG ( R b / Lb) Figure 9. Graphical portrayal of treatment effect estimates. points for each group with post-treatment log sweat ratio Pii = 1og(Rp/Lp) plotted on the vertical axis and baseline log sweat ratio Bij = 1og(Rb/L b) plotted on the horizontal axis. The mean Pij and Bij values for each group are located at the center of gravity (centroid) of each ellipse. The POSTRT treatment effect, Tp, is half the vertical distance between the centroids of the two ellipses. If45 ø lines are drawn through each centroid, the CHGBAS treatment effect, T c, will be half the vertical difference between these two lines. In Figure 9, the estimate is shown at the average baseline ratio, L•, on the horizontal axis. If regression lines with slope b are drawn through each centroid, the ANCOVA treat- ment effect, T a, will be half the vertical difference between the two regression lines. In Figure 9 the estimate is shown at L• on the horizontal axis. Figure 9 portrays the situation where the Tc Tp. If the upper ellipse is moved to the
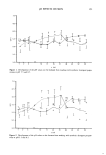
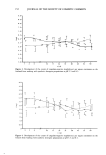
ANTIPERSPIRANT RESULTS 187 right of the lower ellipse, then Tp T c. Note that if the baseline difference between groups is zero, all three estimates, Tp, Tc, and T a, will be identical. The ANCOVA estimate will lie numerically between the CHGBAS and POSTRT estimates when 0 b 1, which is almost always the case for antiperspirant studies. If the slope is close to zero, then Ta will agree more with Tp than with T c. If the slope is close to unity, then T• will be closer in value to T c. A critical assumption is that the regression line for group 1 is parallel to that for group 2. COMPARISON OF THE THREE METHODS To compare the performance of the three estimators, statistical analyses were performed on 70 past clinical studies with baseline measurements. In Table II, the standard deviations of the three-treatment effect estimates are displayed, along with the baseline standard deviation and ANCOVA slope estimate. The pooled standard deviation esti- mates and variances were as follows for baselines (BASLIN) and the three post-treatment methods: Method Standard deviation Variance BASLIN 0.105 0.011005 POSTRT 0.138 0.019044 CHGBAS 0.135 0.018222 ANCOVA 0.125 0.015630 The CHGBAS method was slightly better than the POSTRT method overall, with a 4% variance decrease. Figure 10 shows the ratio of the POSTRT to CHGBAS standard deviation over the 70 studies. About 60% of the time the CHGBAS method gave lower standard deviations values than POSTRT (ratio 1). This result is in contradiction to MacLennan and Whinney (10), who reported that "the inclusion of pre-treatment data nearly always reduces that error variance." The ANCOVA method averaged 14% lower in variance than CHGBAS and 17% lower than POSTRT. Figures 11 and 12 show the standard deviation ratios of POSTRT to ANCOVA, and CHGBAS to ANCOVA. These figures show excursions up to 1.4 in ratio (about twice the variance ratio), indicating that either POSTRT and/or CHGBAS can fail badly in precision relative to ANCOVA for any given study. ANCOVA never fails badly in precision relative to either POSTRT or CHGBAS. Thus, ANCOVA is a more stable procedure with respect to variance, guaranteeing the best precision of the three methods. In six studies, the standard deviation estimates for ANCOVA were slightly higher than for CHGBAS, about 2% higher. In theory, the ANCOVA precision will always be better than that for CHGBAS, but in the estimation of standard deviation, the divisor (degrees of freedom) for the ANCOVA estimate will be one less than the divisor for the CHGBAS estimate since one degree of freedom is removed for the slope estimate. For small studies this difference can be numerically important (5% for 19 versus 20 degrees of freedom). Thus the estimated precision for ANCOVA may be slightly lower than the CHGBAS estimate for studies with a small panel, but this difference will be slight. The slope estimates varied in a range of - 0.15 to 1.16, with an average slope estimate
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)