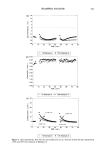
KINETICS OF HAIR REDUCTION 297 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.2 0.1 //.• ,, - - TYPE //')/,'/ --- TYPE TYPE t I I I I 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 •/•0.5 0.0 • • 3.0 3.5 4.0 Figure 15. Reduced-time plot showing a summary of the various experimental kinetic behaviors that have been encountered during this work. 1.0 0.9 - 0.8- 0.7- 0.6 - 0.5 - 0.4 0.5 0.2 0,1 0.0 0.0 TYPE 4 Moving Boundary 0.,5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 ,.3.0 ,3.5 t/to. 5 Figure 16. Reduced-time plot comparing the Type 4 experimental behavior to the theoretical curve for Wickett's moving boundary model. ing us to identify the various experimental behaviors that we may encounter. At present, we have been able to identify the presence of five different behaviors, but we have been unable to determine their significance, or predict when a given behavior would be expected to occur. We have looked for relationships between characteristics of the hair fibers (diameter, cystine content), the rate of the overall reaction (i.e., "easy to perm"/
298 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS "difficult to perm" nature), and the kinetic behavior, but none have been found. It is clear that the kinetic pathway can be altered by changing the properties of the reducing agent solution (pH, concentration) and is also highly sensitive to various hair types. It is hoped that further work will provide a clearer picture of this complex issue. Nevertheless, despite the reservations expressed concerning the basic assumptions of the method, it is shown that the reduced-time treatment is very useful in analyzing the information that is obtained from the SFTK experiments. Results have shown that the reason a hair type may be described as "difficult to perm" is a slower rate of reduction, which then results in a breaking of an insufficient amount of disulfide bonds to give a good curl strength. It has also been postulated by Wickett that a diffusion-controlled process will impart more damage to the hair as a result of the reaction being concen- trated in the outer portions of the fibers. As such, the SFTK technique, together with the ABD-F fluorescence microscopy, can be very valuable in designing new and more effective perms. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors thank Loralei Brandt, Dr. Craig Herb, Elaine LaMarre, Vera Stulov, and Dr. Priscilla Walling. REFERENCES (1) R. R. Wickett, Kinetic studies of hair reduction using a single fiber technique,J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 34, 301-316 (1983). (2) C. E. Reese and H. Eyring, Mechanical properties and the structure of hair, Textile Res. J., 20, 743-750 (1950). (3) R. R. Wickerr and R. Mermelstein, Single fiber stress decay studies of hair reduction and depilation, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 37, 461-473 (1986). (4) R. R. Wickett and B. G. Barman, Factors affecting the kinetics of disulfide bond reduction in hair, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 36, 75-86 (1985). (5) J. Sikorski and H. J. Woods, The effect of rate of extension on the Young's modulus of keratin fibers, Leeds Phil. Soc., 5, 313 (1950). (6) E.G. Bendit, There is no Hookean region in the stress-strain curve ofkeratin,Jo Macrotool. Sci.-Phys., B17(1), 129-140 (1980). (7) C. M. Bamford and C. F. H. Tipper, Eds., Comprehensive Chemical Kinetics, Vol. 22 (Elsevier, Am- sterdam, Oxford, New York, 1980). (8) J. H. Sharp, C. W. Brindley, and B. N. N. Achar, Numerical data for some commonly used solid state reaction equations, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 49, 379-382, (1966). (9) L. F. Jones, D. Dollimore, and T. Nicklin, Comparison of experimental kinetic decomposition data with master data using a linear plot method, Thermochim. Acta, 13, 240-245, (1975). (10) T. Toy'oka and I. Kazuhiro, New fluorgenic reagent having halogenbenzofurazan structure for thioIs: 4-(aminosulfonyl)-7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, Analyt. Chem., 56, 2461-2464 (1984). (11) D. J. Evans, A method for determining the penetration of reducing agents into wool using fluores- cence microscopy, Textile Res. J. 59, 569-579 (1989).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)