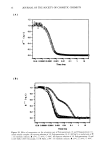
ORGANOFUNCTIONALIZED SILICONE RESINS 15 Table VI Results of Luster Evaluations on Caucasian and Oriental Hair Types Treatment Caucasian Oriental Untreated control 2.9 3.0 Commercial shine spray 3.3 3.2 Protein shine enhancer 2.6 -- Commercial cuticle coat 3.0 Cuticle coat, Formulation 2 3.5 4.5 containing the styryl-modified resin consistently rated higher in shine evaluations than the other products, with averages of 21 and 50 percent higher ratings for Caucasian and Oriental hair types, respectively, as compared to the untreated controls. SUBSTANTIVITY The last series of materials evaluated in this study were the ester-modified siloxysilicate resins. Table II lists some of the typical acids and alcohols utilized in preparing the esters that were subsequently grafted onto the siloxysiticate resins. Combinations involving saturated alcohols and unsaturated organic acids resulted in stable products that were not found to offer any performance benefits. Combinations involving short-chain unsaturat- ed alcohols (e.g., allyl alcohol) and saturated organic acids resulted in unstable products. Materials obtained from the reaction of a saturated acid with a long-chain, branched, unsaturated alcohol were characterized as being stable and providing some interesting performance benefits. Based on the data above, trimethylolpropane monoallyl ether (TMPMAE) became the alcohol of choice, and this material was reacted with linear and branched acids of varying chain lengths. The melting point and physical forms of several siloxysilicate resins modified with the resulting esters are listed in Table VII below. During cursory evaluations with these compounds, it was observed that the ester- modified resins were somewhat substantive to skin. To further evaluate substantivity properties of the various ester-functional siloxysilicates, a modified ASTM spray test method was utilized. The ester-functional resins showed enhanced substantivity and water resistance in this evaluation as compared to the other fluids tested, as demon- strated in Figure 6. The low-viscosity dimethicone fluid was completely removed after one spray cycle. The organic ester and the unmodified silicone resin were both com- pletely removed after four cycles, while the C•2 and C•6 ester-modified resins were present at 15% and 25%, respectively, after six wash cycles. The C•s isostearyl- functional resin was slightly more substantive during the first few spray cycles, but by Table VII Melting Points and Physical Forms of Siloxysilicate Resins Modified With Various Organic Esters Acid chain length Melting point (øC) Physical form Lauric (C• 2) - 25 Liquid Myristic (C•4) + 5 Liquid Palmitic (C•6) + 20 Liquid Stearic (C•8) + 35 Hard wax Isostearic (C• 8) -40 Liquid
16 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS lOO 9o 8o 7o 6o 4o 3o 2o lO o • PDMS --•--IPM '--A--MQ ---N--C10MQ • C12MQ '-e--C18MQ ! ! 0 I 2 3 4 5 Spray Cycles Figure 6. Comparison of substantivity on polycarbonate slides for dimethicone, isopropyl myristate, un- modified silicone resin, and siloxysilicate resins modified with ester groups containing 10, 12, and 18 (isostearyl) carbon atoms per chain. completion of the sixth rinse it proved to be equivalent to the C•6 straight-chain compound. The C•2 or the C•8 isostearyl ester-modified siloxysilicates were evaluated in water resistance and SPF studies conducted at an independent laboratory. These materials were applied out of a prototype sunscreen formulation and were compared to a control composition containing an organic ester, octyl palmitate. All three of the formulations were characterized by initial SPF values of 15, as can be seen in Table VIII. The results indicate a slight removal of the formulation containing the C•2 silicone ester after 40-min exposure in water, with the initial SPF 15 value dropping to 13.5. A further decrease in the SFP value to 12 was observed after the subjects were submerged for 80 min. The C•8 ester-modified siloxysilicate and the organic ester were both found to be more substantive than the C• material in this particular formulation. Both the octyl palmirate and C•8 isostearyl ester-modified siloxysilicate demonstrated water resistance properties as evidenced by unchanged SPF values following a 40-min exposure in warm Table VIII SPF Values of Prototype Sunscreen Formulations With Organic or Silicone Esters Time C•2M Q C•8M Q Octyl palmitate 0 15 15 15 40 min 13.5 15 15 80 min 12 13 13
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)