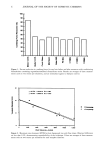
68 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS The most important program concerning the Frequency of Use of Preservatives is the Voluntary Filing of Cosmetic Product Ingredient and Cosmetic Raw Material Composition Statements (Part 720). The manufacturer files Form FDA 2512 (Cosmetic Product Ingredient Statement) with the FDA. There is no filing fee. FDA Form 2514 (Discontinuance of Commercial Distribution of Cosmetic Product Formulation) is used to remove a formulation. Up to 1992, the intended use of each ingredient must be specified as either color, fragrance, presen, ative or other. As a result, many products were checked off as being preservatives. when they really were incorporated for other reasons. Also, chemicals which were actually preservatives, might have been marked as other. The FDA did not edit any of these uses. Frequency of Use of Preservatives 1996 Table 1 list the Frequency of use of Preservatives from the 19,150 current formulations registered with the FDA in 1996. Although this is for cosmetic formulations, it is clear from the dam, that many OTC drugs are included. The Agency receives about 200 forms for listing and deleting formulations, each month. Table 1. Preservatives by Frequency of Use Preservative 1996 1993 1992 1990 1987 total Number of Formulations 19,150 NA 20,351 20,035 18,850 Methylparaben 7731 6738 8288 7754 7306 Propylparaben 6278 5400 6632 6343 6030 lmidazolidinyl urea 2498 2312 2481 2749 2499 Butylparaben 1991 1669 1343 1200 1072 Ethylparaben 1240 1213 853 810 581 Phenoxyethanol 1143 929 674 375 253 DMDM Hydantoin 955 747 773 550 318 Methylchloroisothiazolinone/Methylisothiazolimone 808 1042 637 711 512 Sodium Sultite 789 558 NA 64 64 Quatemium-15 704 639 898 705 673 Diazolidi ,nyl Urea 690 466 427 280 130 So•bic Acid/Potassium Sotbate 484 363 NA 256 296 Triclosan 459 359 356 181 138 Deh•droacetic Acid/Sodium Dehydroacetate 456 321 NA 383 375 Benzol Alcohol 417 237 NA 64 86 Benzoic Acid/Sodium Benzoate 378 265 NA 200 226 Sodium Borate 375 358 NA 29 29 2-Bromo-2-Nitropropane- 1,3-Diol 210 223 305 321 317 Formalin (includes paraformaldehyde) 187 228 NA 463 494 [sobutylparaben 125 89 NA 38 26 Iodopropynyl Butylcarbamate 122 0 0 0 0 Boric Acid 101 106 NA 26 28 Salicylic Acid 101 82 NA 23 26 Benzalkonium Chloride 96 86 199 161 41 •hloroacetamide 76 75 NA 82 40 Sodium Bisulfite 68 48 Na 55 43 Methenamine 67 0 NA 1 1 Benzethonium Chloride 59 55 NA 23 20 Methyldibromo Glutaronitrile 57 22 4 0 0 •hloroxylenol 46 49 NA 55 47 •lutaraldehyde (Glutaral) 46 61 NA 41 39 Hexamidine Isethionate 45 0 NA 5 0 5-Bromo-5 -Nitro- 1,3 -Dioxane 40 60 NA 58 44 Sodium Methylparaben 38 0 NA 21 18 Ehlorhexidine Digluconate 37 27 NA 18 13 Phenethyl Alcohol 37 NA NA 8 8 •-Phenylphenol/sodium o-Phenylphenol 36 8 NA 15 20 rriclocarban 22 0 NA 4 3
PREPRINTS OF THE 1997 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 69 Sodium Hydroxymethylglycinate 19 2 2 0 0 Polymethoxy Bicyclic Oxazolidine 18 0 NA 0 0 Chlorhexidine Dihydrochloride 16 0 NA 5 5 Dimethoxane 16 20 qA 19 23 p-Chloro-m-Cre,sol 1•5 0 C 0 0 Phenyl Mercuric Acetate 14 20 qA 35 35 Isopropylparaben IC 4 qA 9 12 Chlorhexidine Acetate 9 0 qA 3 C Thimerosal 9 11 qA 21 22 Dichlorobenzyl Alcohol 8 11 qA 12 4 Captan ? 11 NA 19 3C Chlorphenesin 7 0 NA 0 • Domiphen Bromide ? 0 NA 4 2 Dichlorphene 5 0 NA 3 3 Phenoxyisopropanol 5 0 NA 5 5 Sodium Propylparaben 5 0 NA 0 0 Polyaminopropyl Biguanide 4 0 0 0 • Benzylparaben 0 95 NA 9 9 Chlorbutanol 0 0 NA I I THE ROLES OF SURFACTANTS• SOLUBLE POLYMERS• AND SURFACTANT- POLYMER COMPLEXES IN COSMETIC PRODUCTS Wil Hemker Salient Science, Inc., Middleburg Hts., OH 44130 USA Surfactants, soluble polymers, and/or surfactant - polymer complexes are fundamental ingredients to nearly every fluid personal care product: suspensions, emulsions, and foams. Why? They provide the desired viscosity, stability, and delivery of a product to the site of action: skin hair nails or teeth ...'surfaces'. Surfaces that need cleaning, conditioning, moisturizing, protecting, or coloring in the most effective, mild, and sensory-attractive way. Surfaces and interfaces are where these ingredients are the most active to stabilize emulsions / suspensions and deliver functional ingredients. Formulating to maximize stabilization, delivery, and mildness can often work at cross purposes. Surfactants, typically lOO0 mw, adsorb at interfaces to physically reduce surface energies for wetting / spreading and self associate as micelies or lyotrophic liquid crystals (LC) to alter the rheology and stabilize liquid suspensions. Water soluble polymers, typically lO,000 mw, can adsorb at interfaces (chemistry dependent) to lubricate, stabilize suspensions, or deposit a film. Surfactant - polymer complexes, fundamental structures in biological systems, recently have been more extensively studied. Binding is strongest involving electrostatic forces. Complexes as single phase solutions or multiphase suspensions are central to "multi-functional products" e.g. cleansers / conditioners, cleansers / moisturizers or controlled delivery activity.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)