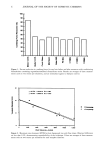
ORGANOFUNCTIONALIZED SILICONE RESINS 7 deviations in the readings. Thus great care was taken to insure an undisturbed atmo- sphere during the volume experiments. LUSTER EVALUATIONS Luster evaluations were performed on 6-in 3-g tresses of virgin medium-brown Cauca- sian and untreated Oriental hair obtained from DeMeo Bros. The styryl-modified si- 1oxysilicate resin was formulated into a cuticle coat conditioning product as shown in Formulation 2 listed in Appendix A. This composition was used in luster evaluations on Caucasian and Oriental hair types and was compared to tresses treated with 1) a com- mercial shine spray containing dimethicone gum, cyclomethicone, and several organic oils, 2) a commercial cuticle coat composition containing dimethicone and phenyltri- methicone, or 3) a protein-based shine enhancer product. The cuticle coat formulations were applied by first placing two drops on the palm of the hand, rubbing the hands together, and then working through the tresses. The shine spray was applied from a distance of 6 in, depressing the actuator valve three times per side, and delivering a total of 0.6 g of product per tress. The protein-based shine enhancer was used at a level of 0.37 g/2 g tress and worked through the hair according to the package directions. All tresses were air dried for 2 hr prior to evaluations. Luster evaluations were performed by an independent salon operator and an in-house panel of 23 participants. Panelists were asked to compare the treated tresses to untreated controls and then to rate shine on a scale of 1-5. Two reference standards were provided for their benefit: relaxed African- American hair soaked in hexane for 15 min representing a dull standard, or a value of 1 on this scale, and untreated Oriental hair dipped in mineral oil depicting a tress possessing a high degree of shine, characterized by a 5 on the luster scale. CURL RETENTION MEASUREMENTS The use of unmodified siloxysilicate or MQ resins in hair fixative applications is known in the art (27). To determine the effect organomodification of the silicone resin would have on set properties, curl retention studies were carried out using the unfunctionalized siloxysilicate materials and several of the modified resins. Included in this test was a water-set control, an unmodified MQ resin, the three alkyl-modified siloxysilicates, an isostearyl ester-modified MQ, and a polyether-functional resin (EO-modified). Set re- tention evaluations were performed by shampooing the hair twice, then applying a 10% active dilution of the silicone resins to the wet hair. The polyether-modified resin was diluted in water while the unmodified and alkyl-functional siloxysilicates were diluted to 10% active solutions in cyclomethicone. The ester-functional compound was applied from a 10% dilution in an aliphatic hydrocarbon solvent. A water-set control tress was included in this experiment for comparison purposes. The shampooed tresses were dipped into the various solutions, wound around a glass rod of 1/2-inch diameter, the ends being secured with rubber bands, and allowed to condition overnight at 50% RH and 25øC (+/-2øC) prior to curl evaluations. Measurements were taken at set intervals over a 24-hr period, and percent curl retention was calculated according to the formula: % Curl retention - -- x 100%
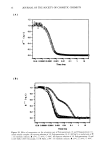
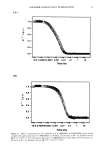
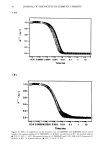
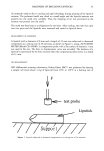
8 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS where L o is the length of the tress at time 0, L• is the initial length of the tress, and L t is the length of the tress at time t. SUBSTANTIVITY EVALUATIONS Substantivity of three ester-modified MQ resins was evaluated by a modified spray method (ASTM•D 1913). This test method describes a procedure used to measure water resistance of hydrophobically modified cloth (see apparatus detail in Figure 3). In the tests performed with the silicone resins, the cloth sample was replaced with poly- carbonate slides on which three drops of test material were applied and evenly spread over the slide with a finger cot. The substances evaluated in this study included silicone resins modified with C•2, C•6, and C•8 (isostearyl) ester groups. Also included in this study, for comparison purposes, were a dimethicone fluid of 350 cst viscosity, an unmodified MQ resin, and an organic ester, isopropyl myristate. Substantivity tests were performed using neat fluids. Rinse cycles consisted of 250-cc aliquots of water, each equilibrated to ambient temperature. Slides were air dried and evaluated visually be- tween each rinse cycle. Two of the ester-modified resins (C•2 and C•8 isostearyl) were then formulated into a prototype sunscreen composition given in Appendix A, Formulation 3, and sent to an independent testing facility for evaluation of SPF values and water resistance properties. A control formulation in which the silicone ester had been replaced with an organic ester, octyl palmirate, was also provided. These evaluations were performed on three panelists characterized as having skin type II or III (see Table IV for skin type classi- fications), using a Xenon arc solar simulator as the ultraviolet light source. Procedures were carried out according to the methods described in the FDA monograph for SPF determinations and water-resistance evaluations. On the first day of the test, fresh product was applied to the panelists' backs and allowed to air dry. The panelists were then irradiated and sent home. Initial SPF values were measured the next day. The sunscreens were then freshly applied to the panelists, who were submerged, after the product had air dried, for 40 rain in warm turbid water, removed for 20 min, allowed to air dry, and then irradiated this process was repeated once more for the 80-min evaluation. The panelists returned the next day and SPF values were measured again. The same two ester-modified siloxysilicate resins were formulated into lipsticks, as shown in Formulation 4 listed in Appendix A, in order to evaluate substantivity prop- erties and reduction of pigment transfer from color cosmetics. A panel of in-house participants was asked to apply each product to half of their lips, both top and bottom. After a 60-sec set time, the panelists blotted their lips on tissue and the amount of pigment transfer was evaluated visually. They were then instructed to reapply the two products and wear them for the rest of the day, making observations on wear charac- teristics and feathering or skin-bleeding properties. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION COMBING ANt) VOLUM• It is known in the art that increasing the organoalkyl content of quaternary ammonium
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)