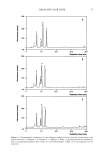
SKIN DAMAGE PROTECTION BY PRUNUS PERSICA 29 the dried residue was mixed with an oil-based vehicle and applied to the animal skin. For isolating the constituents, the residue was dissolved in a small amount of methanol. The dissolved residue was poured into a silica gel column and eluted with chloroform: methanol:water (10:3:0.5) as a mobile phase, giving ten subfractions. Subfraction 7 was dried and further separated in the RP-18 column using methanol:water (1:1), giving compound I. From subfraction 5, the repeated silica gel column chromatography yielded compound II. From subfraction 4, the repeated silica gel column chromatography and subsequent separation with the RP-18 column using methanol:water (55:45) gave com- pounds III and IV. Compound I: Recrystallized from methanol (yellowish amorphous powder). 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) • 12.61 (s, 1H, 5-OH), 7.76 (d, 2H, J = 8.6 Hz, H-2' and 6'), 6.93 (d, 2H, J = 8.6 Hz, H-3' and 5'), 6.41 (s, 1H, H-8), 6.21 (s, 1H, H-6), 5.18 (s, 1H, rhamnosyl anomeric H), 4.30 (d, 1H, J = 8.0 Hz, glucosyl anomeric H), 0.90 (d, 3H, J = 5.6 Hz, rhamnosyl-CH3). For 13C-NMR, see Table I. Acid hydrolysis products: kaempferol, glucose, rhamnose. Compound II: Recrystallized from methanol (yellowish platelets), m.p. -- 233ø-235øC, 1H-NMR (DMSO-d 6) B 12.70 (brs, 1H, 5-OH), 8.06 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, H-2' and 6'), 6.86 (d, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, H-3' and 5'), 6.42 (d, 1H, J -- 2.0 Hz, H-8), 6.19 (d, 1H, J -- 2.0 Hz, H-6), 5.40 (d, 1H, J = 7.6 Hz, galactosyl anomeric H). Acid hydrolysis products: kaempferol, galactose. Compound III: Recrystallized from acetone (yellowish needles), m.p. = 174ø-177øC, 1H-NMR (DMSO-d 6) B 12.63 (s, 1H, 5-OH), 7.75 (d, 2H, J = 8.6 Hz, H-2' and 6'), 6.91 (d, 2H, J = 8.6 Hz, H-3' and 5'), 6.41 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, H-8), 6.20 (d, 1H, J = 2.0 Hz, H-6), 5.29 (s, 1H, rhamnosyl anomeric H), 0.78 (d, 3H, J = 5.5 Hz, rhamnosyl-CH3). Acid hydrolysis products: kaempferol, rhamnose. Compound IV: Recrystallized from acetone (yellowish prisms), m.p. 250øC, 1H-NMR (DMSO-d6) B 12.61 (brs, 1H, 5-OH), 8.04 (d, 2H, J = 8.8 Hz, H-2' and 6'), 6.88 (d, 2H, J -- 8.8 Hz, H-3' and 5'), 6.42 (s, 1H, H-8), 6.20 (s, 1H, H-6), 5.45 (d, 1H, J = 7.0 Hz, glucosyl anomeric H). Acid hydrolysis products: kaempferol, glucose. HPLC ANALYSIS The contents of the isolated fiavonoids in crude extract (Ku-35) were measured using HPLC (Shimadzu, Japan) equipped with a reverse-phase ODS-II column (4.6 x 150 mm, Shinwa Chem.) and UV360 nm. The solvent gradient [3%•90%, 1% acetic acid in water: 1% acetic acid in acetonitrile] was used as a mobile phase at 1 ml/min for 75 min. The retention times for compounds I-IV were found to be 34.6, 38.3, 33.2, and 36.3 min, respectively. IN VIVO ERYTHEMA TEST Dorsal hairs of guinea pigs were shaved and depilated by application of Nair ©. After 4 hr, the plastic film having six circular holes was wrapped with rubber bands around each animal. Test compounds, including Ku-35 pre-mixed with an oil-based vehicle, were applied (20 mg of compound plus vehicle/1.1 cm2/site). Control sites received only 20 mg of vehicle/site. Five hours later, the sites were irradiated with UVB (1 J/cm 2,
30 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table I t•C-NMR Assignments of the Isolated Flavonoid Derivatives Compound I II III IV C-2 157.3 • 156.4 a 157.3 3 134.5 133.2 134.2 4 177.8 177.5 177.8 5 161.4 161.2 161.4 6 98.9 98.8 98.8 7 164.6 164.2 164.5 8 93.9 93.7 93.8 9 156.6 • 156.3 a 156.6 10 104.1 103.8 104.1 1' 120.6 120.9 120.6 2' 130.7 131.0 130.7 3' 115.5 115.0 115.4 4' 160.1 159.9 160.0 5' 115.5 115.0 115.4 6' 130.7 131.0 130.7 Rham-1 102.0 101.8 2 70.3 b 70.1 3 69.8 b 70.3 4 82.0 71.1 5 69.0 b 70.7 6 17.3 17.5 Glu-1 104.8 2 74.5 3 76.7 c 4 69.8 • 5 77.0 c 6 61.0 Gal-1 101.7 2 71.2 3 73.1 4 67.9 5 75.8 6 60.2 156.5 133.2 177.5 161.2 98.8 164.5 93.7 156.2 103.9 121.0 130.9 115.1 160.0 115.1 130.9 100.9 74.2 77.5 e 69.9 76.4 e 60.8 All NMR spectrums were measured in DMSO-d 6. a,b,c,d,e Interchangeable values in each column. irradiation time: 3 min) and the formation of erythema was observed regularly up to 72 hr according to the criteria previously described (5). IN VIVO EAR EDEMA TEST Ku-35 pre-mixed with an oil-based vehicle was applied to the ears of mice. After 1 hr, mice lightly anesthetized with ether were irradiated with UVB (4 J/cm 2, irradiation time: 12 min). Twenty hours later, the ear thickness of each mouse was measured with a dial thickness gauge (Lux Scientific Instrument, USA) after washing out the applied vehicle. The increase in ear thickness after UV irradiation was regarded as edema formation. STATISTICS All data were represented as arithmetic mean + S.D. The statistical significance was
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)