48 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE +l • +l +1 +l +l .... 04 +l +1 +l +l +l +l
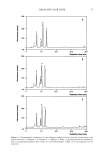
OXIDATIVE HAIR DYES 49 2OOO 1500 -- 1000 -- 500 -- -150 5 6 I I 0 7.5 15.0 I 22.5 30.0 Retention time (min) 2000 1500_ 1000 - 500 _ 1 3 5 -150 I I I 0 7.5 15.0 22.5 30.0 Retention time (min) Figure 1. Chromatographic separations of two synthetic formulations after matrix extraction. a: "light brown." b: "light blonde." Peaks: (1) NaAsc (intrinsic matrix, antioxidant), (2) matrix compound, (3) p-phenylenediamine, (4) m-phenylenediamine sulfate, (5) m-aminophenol, and (6) resorcinol. See text for experimental data and acronyms. compounds in pure standard solutions commonly found in oxidative hair dye formula- tions (9), the identification could then be performed by comparison between the ex- perimental data obtained and the recorded data. Table II and Figure 2 show the iden- tification obtained by combining the two criteria retention time and UV spectra. Peaks 3, 4, 5, and 6 are attributed to p-phenylenediamine, m-phenylenediamine sulfate, m- aminophenol, and resorcinol, respectively. Peaks 1 (attributed to sodium ascorbate) and 2, having retention times shorter than 5 min, are due to remaining matrix compounds not interfering with the dye separation, in accordance with previous observations (2,3).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)