82 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE for days at a time." Indeed, Rp is so adherent that it has been used as a vaginal drug delivery system (5). To date, only one piece of evidence supports the hypothesis that bioadherence of the carbomer-polycarbophil is not important in the relief of vaginal dryness. While Bach- man et aL (6) report that this bioadhesion holds water in place on the vaginal epithelium, they also report as little as 7.8% vaginal residue in women using Rp, after five con- secutive days of use. This suggests that bioadhesion of polycarbophil is not necessary for relief of vaginal dryness. A new product, Summer's Eve © (SE) vaginal moisturizer, avoids the use of bioadhesives by using pectin while providing natural moisturizers to relieve vaginal dryness. This clinical study was designed to compare the patient-perceived vaginal moisturization properties of Rp to those of SE and to evaluate the amount of vaginal residue resulting from the use of each product in a double-blind crossover study. MATERIALS AND METHODS PATIENTS Fifty-one postmenopausal patients aged 41-67 (mean age 52) who met all study inclu- sion and exclusion criteria (Table I) were admitted into the study. The study began on April 1, 1999, and ended on May 14, 1999. The two products tested in this study are described in the literature. Each patient was randomly allocated to a treatment group. Each group went through a one-week washout period, during which time no sexual lubricant/moisturizer was used. Group A used SE vaginal moisturizer every other day for two weeks, avoided the use of any lubricant for one week, and then used Rp every other day for two weeks. Group B used Rp every other day for two weeks, avoided the use of any lubricant for one week, and then used SE vaginal moisturizer every other day for two weeks. The use of each Table I Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Inclusion criteria Exclusion criteria Healthy females, aged 40 years and older who report vaginal dryness due to perimenopause, menopause, or oophorectomies Females who normally have sexual intercourse at least once per week Absence of history or visible evidence of chronic skin disease or regional infection Dependability and intelligence to follow directions Willingness to cooperate No history of sensitivity to similar formulations Completion of medical history form Understanding and execution of the informed consent agreement Females who have any disease or condition that, in the opinion of the gynecologist, could affect the test results Females using hormonal replacement therapy Females with a history of genital herpes, recurrent vaginal infections, or urinary bladder infections Females using medications that might influence the test results Females with a history of allergy or hypersensitivity to any female hygiene product
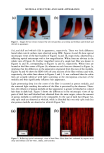
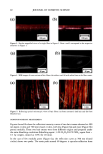
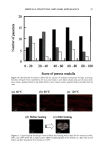
PECTIN-BASED VAGINAL MOISTURIZER 83 product in this study was consistent with the stated directions for use on each package. The ingredients for each vaginal moisturizer are shown in Table II. The study protocol for an almost identical study and the informed consent agreement used in this study were approved by an IRB prior to initiation of the study. METHODOLOGY Each potential patient's suitability for the study was reviewed (Table I). Those who passed the initial screening completed an informed consent agreement before admission into the study. Each panelist underwent a complete gynecological examination by a board-certified gynecologist for signs of erythema, edema, and any vaginal or perineal inflammation or irritation. The examination included the use of a colposcope for visu- alization of the entire vaginal wall. The initial findings of the vaginal/perineal exami- nation had to be within the normal range for the patient to continue in the study. I,terva/I. After a one-week washout period, during which the patient was not allowed to use any type of vaginal lubricant/moisturizer, the patients returned for another complete gynecological examination as described above, with one addition. The gyne- cologist's examination included an observation for evidence of vaginal residue. Residue was noted by location and approximate amount (0 = none 1 -- minimal 2 = mild 3 = moderate 4 = significant). Each patient received a test product according to the ran- domization code and a daily diary to document compliance with the study requirements. After two weeks of product usage every other day, the patients returned unused product to the clinic along with their diaries. Their diaries were reviewed for completeness. Each patient was required to complete an evaluation form assessing the product's overall acceptability and efficacy. Gynecological examinations were repeated as described above, including an observation for evidence of product residue. I,terva/II. During the one-week washout period between intervals, patients douched with Summer's Eve Ultra and were not allowed to use any type of vaginal lubricant/ moisturizer. After this one-week washout, the patients returned for another complete gynecological examination, as described above, including an observation for evidence of Table II Ingredients in Each of the Two Vaginal Moisturizers, Rp and SE Rp SE Purified water Purified water Glycerin Propylene glycol Mineral oil Methylcellulose Polycarbophil Xanthan gum Carbomer 934P Sodium lactate Hydrogenated palm oil glyceride Methylparaben Sorbic acid Lactic acid Methylparaben Dextrose Sodium hydroxide Sodium chloride Edetate disodium Pectin Propylparaben
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)