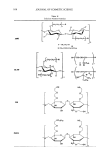
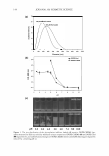
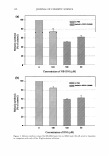
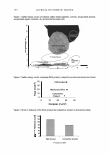
124 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE CONCLUSION The present study demonstrates that HMF inhibits not only tyrosinase activity (Figure 4) but also its gene expression (Figure 3). This unique dual mechanism of HMF may explain why this compound is so effective in the prevention of cellular melanogenesis (Figure 2). HMF may be useful for the prevention of undesired skin pigmentation. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by a BioMedical Research Institute grant from Kyungpook National University Hospital (2005). This work was also supported by the Brain Korea 21 Project (2006). REFERENCES (1) J. S. Mas, I. Gerritsen, C. Hahmann, C. Jimenez-Cervantes, and J. C. Garcia-Borron, Rate limiting factors in melanocortin 1 receptor signalling through the cAMP pathway, Pigment Cell Res., 16, 540-547 (2003). (2) R. Busca and R. Ballotti, Cyclic AMP, a key messenger in the regulation of skin pigmentation, Pigment Cell Res., 13, 60-69 (2000). (3) K. Yasumoto, K. Yokoyama, K. Takahashi, Y. Tomita, and S. Shibahara, Functional analysis of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor in pigment cell-specific transcription of the human tyrosinase family genes,]. Biol. Chem., 272, 503-509 (1997). (4) R. A. Spritz, L. Ho, M. Furumura, and V. J. Hearing, Jr., Mutational analysis of copper binding by human tyrosinase,j. Invest. Dermatol., 109, 207-212 (1997). (5) R. Balaban, E. Cheng, and D. N. Hebert, Coexpression of wild-type tyrosinase enhances maturation of temperature-sensitive tyrosinase mutants, J. Invest. Dermatol., 119, 481--488 (2002). (6) H. Y. Park, J. M. Perez, R. Laursen, M. Hara, and B. A. Gilchrest, Protein kinase C-beta activates tyrosinase by phosphorylating serine residues in its cytoplasmic domain,]. Biol. Chem., 274, 16470- 16478 (1999). (7) C. Jimenez-Cervantes, J. C. Garcia-Borron, P. Valverde, F. Solano, and J. A. Lozano, Tyrosinase isoenzymes in mammalian melanocytes. 1. Biochemical characterization of two melanosomal tyrosi- nases from B16 mouse melanoma, Eur. J. Biochem., 217, 549-556 (1993). (8) S. Briganti, E. Camera, and M. Picardo, Chemical and instrumental approaches to treat hyperpig- mentation, Pigment Cell Res., 16, 101-110 (2003). (9) K. S. Kim, J. A. Kim, S. Y. Born, S. H. Lee, K. R. Min, and Y. Kim, Inhibitory effect of piperlon- guminine on melanin production in melanoma B 16 cell line by downregulation of tyrosinase expres- sion, Pigment Cell Res., 19, 90-98 (2006). (10) K. Nakamura, M. Yoshida, H. Uchiwa, Y. Kawa, and M. Mizoguchi, Down-regulation of melanin synthesis by a biphenyl derivative and its mechanism, Pigment Cell Res., 16, 494-500 (2003). (11) E. V. Curto, C. Kwong, H. Hermersdorfer, H. Glatt, C. Santis, V. Virador, V. J. Hearing, Jr., and T. P. Dooley, Inhibitors of mammalian melanocyte tyrosinase: In vitro comparisons of alkyl esters of gentisic acid with other putative inhibitors, Biochem. Pharmacol., 57, 663-672 (1999). (12) M. Funayama, H. Arakawa, R. Yamamoto, T. Nishino, T. Shin, and S. Murao, Effects of alpha- and beta-arbutin on activity of tyrosinases from mushroom and mouse melanoma, Biosci. Biotechnol. Bio- chem., 59, 143-144 (1995). (13) R. E. Boissy, M. Visscher, and M. A. DeLong, DeoxyArbutin: a novel reversible tyrosinase inhibitor with effective in vivo skin lightening potency, Exp. Dermatol., 14, 601-608 (2005). (14) Y. C. Boo, C. 0. Jeon, and J. Y. Oh, Isolation of 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3[2H]-furanone from pine needles as an antioxidative principle, Agric. Chem. Biotechnol., 37, 310-314 (1994). (15) Y. C. Boo, C. 0. Jeon, J. Y. Oh, E. J. Kim, and B. G. Lee, Antimelanogenesis effects of 4-hydroxy- 5-methyl-3[2H]-furanone, an antioxidant isolated from pine needles,]. Soc. Cosmet. Scientists Korea, 20, 1-13 (1994).
ANTIMELANOGENIC EFFECTS OF HMF 125 (16) H.J. Kim, S. I. Lee, D.-H. Lee, D. Smith, H. Jo, H. E. Schellhorn, and Y. C. Boo, Ascorbic acid synthesis due to l-gulono-1,4-lactone oxidase expression enhances NO production in endothelial cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 345, 1657-1662 (2006). (17) D. S. Kim, S. Y. Kim, J. H. Chung, K. H. Kim, H. C. Eun, and K. C. Park, Delayed ERK activation by ceramide reduces melanin synthesis in human melanocytes, Cell. Signalling, 14, 779-785 (2002). (18) A. K. Chakraborty, Y. Funasaka, M. Komoto, and M. Ichihashi, Effect of arbutin on melanogenic proteins in human melanocytes, Pigment Cell Res., 11, 206-212 (1998). (19) R. A. Sturm, R. D. Teasdale, and N. F. Box, Human pigmentation genes: Identification, structure and consequences of polymorphic variation, Gene, 277, 49-62 (2001). (20) T. Hauck, C. Landmann, F. Bruhlmann, and W. Schwab, Formation of 5-methyl-4-hydroxy-3[2H]- furanone in cytosolic extracts obtained from Zygosaccharomyces rouxii,J. Agr. Food Chem., 51, 1410- 1414 (2003). (21) S. Kataoka, Functional effects of Japanese style fermented soy sauce (shoyu) and its components, J. Biosci. Bioeng., 100, 227-234 (2005).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)