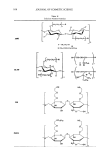
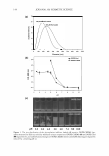
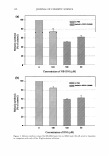
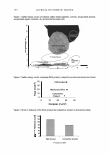
184 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE BOTANICAL ACTJ.VE INGREDIENTS THAT ENHANCE SKIN TONE: AN IN //Jvo STUDY Isabelle Imbert, Ph.D., Claude Dal Farra, Ph.D. and Nouha Domloge Vincience-lnternational Specialty Products INTRODUCTION Desire for a natural tanned skin appearance without excessive UV exposure or the use of irritating self-tanning products has increased consumer interest in tone enhancers (1, 2, 3). These products are also of particular interest to an overall anti-aging strategy, insofar as they protect against premature aging-a direct consequence of photoaging- and against UV-induced damage ( 4, 5). In line with this trend, we have developed a new tone enhancer active ingredient. This new botanical active ingredient has demonstrated significant protective effects against UV-induced damage, with better homogenization of skin tone. METHODOLOGY To investigate the extract's activity, skin tone was evaluated using Fontana-Masson staining on human skin biopsies treated with I% of the active ingredient for 24 hours. For skin biopsies exposed to DVB-irradiation, a 24-hour treatment with I% of the active was also performed. Treatments were applied twice: once before and once after irradiation with 100m.J/cm2 of UVB. In order to evaluate the activity of this active ingredient, secreted IL-1 beta was measured in human fibroblasts 24 hours after treatment with the active ingredient at I% and 3% (ELISA). 20 healthy volunteers of both sexes, age 25 to 55, participated in this double-blind study. Volunteers applied a cream formula with 1.5% of the new extract, or placebo, on the forearm, twice a day for 28 days. Clinical evaluations were performed at the beginning of the study, after one week, and at the end of the study. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A time-dependent and dose-dependent increase in skin tone was observed when skin biopsies were treated for 24 hours with 1 % of the active ingredient applied twice daily (Figure 1 ). In these conditions, irradiated skin biopsies showed higher skin tone intensity than non-irradiated biopsies, and irradiated active-treated biopsies revealed a better homogenization of melanin content than that of irradiated control biopsies. Irradiated and treated fibroblasts exhibited a significant decrease in IL-1 beta level (- 38%, p=0.0171 and -45%, p=0.0022 with 1 % and 3% of the active ingredient, respectively), indicating that this extract can prevent swelling and redness, especially under UVB-stress induction (Figure 2). The new extract showed a rapid action in enhancing skin tone of volunteers, as early as within 7 days of the test. After four weeks, the difference in skin tone between the extract-treated and placebo sides was also highly significant and the results revealed an increase in skin tone of 194.9% on the extract-treated side. This effect was observed in more than 80% of volunteers. The improvement of the extract-treated side was confirmed clinically, and was clearly seen in 75% of volunteers (Figures 3 and 4).
2007 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING Control Control UVB Extract+ UVB Figure 1: Fontana-Masson stauung of human skin biopsies treated with 1 % of the active ingredient for 24 h DO D7 D28 Figure 3: Evolution of skin tone during the study in placebo-treated skin and extract-treated skin - Volunteer A CONCLUSION ::ll Q. Figure 2: IL-1 beta expression in human fibroblasts treated with the extract at 1 % and 3% for 24 h, irradiated with UVB at 1 00mJ/cm2 and treated again for 24 h DO D7 028 Figure 4: Evolution of skin tone du.ring the study in placebo-treated skin and extract- treated skin - Volunteer B 185 Taken together, these results indicate that this new active ingredient can help prevent sun-induced damage by enhancing skin tone and limiting UV-induced skin inflammation. The study thus suggests that this active ingredient can be of great use in skin care, sun care, and self tanning products. REFERENCES 1. J. E. Stryker, A. L. Yaroch, R. P. Moser, A. Atienza, K. Glanz, J Am A cad Dermatol., 56(3), 387-390, 2007. 2. J. K. Rivers, B. Wang, D. Marcoux, J Cutan Med Surg., 10(1), 8-13, 2006. 3. C. Robb-Nicholson, Harv Womens Health Watch, 14(2), 8, 2006. 4. R. Cui, H. R. Widlund, E. Feige, J. Y. Lin, D. L. Wilensky, V. E. Igras, J. D'Orazio, C. Y. Fung, S. R. Granter, D. E. Fisher, Cell, 128(5), 853-864, 2007. 5. S. Freeman, S. Francis, K. Lundahl, T. Bowland, R. P. Dellavalla, Arch Dermatol., 142(4), 460-462, 2006.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)