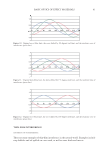
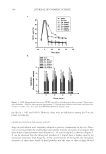
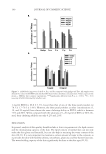
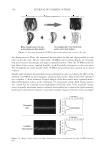
J. Cosmet. Sci., 61, 107–123 (March/April 2010) 107 New alternatives to cosmetics preservation S. PAPAGEORGIOU, A. VARVARESOU, E. TSIRIVAS, and C. DEMETZOS, Laboratory of Cosmetology, Department of Aesthetics and Cosmetology, School of Health & Caring Professions, Technological Educational Institution, Ag. Spyridonos Str., 12210 Egaleo (S.P., A.V., E.T.), Frezyderm S.A., Medicine-Cosmetics, 4 Tatoiou Avenue, 14451 Metamorphosi (S.P.), and Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, School of Pharmacy, University of Athens, Panepistimiopolis, 15771 Zografou (C.D.), Athens, Greece. Accepted for publication August 24, 2009. This work was partially presented at the 7th Joint Meeting of AFRP, ASP, GA, PSE and SIF, Athens, Greece, and at the XIIIth COSMODERM Joint Meeting of ESCAD and the Hellenic Society of Dermatology and Venerology, Athens, Greece. Synopsis In recent years, there is a considerable interest in the development of preservative-free or self-preserving cos- metics. The aim of our work was to develop new cosmetic formulations by replacing chemical preservatives with ingredients with antimicrobial properties that are not legislated as preservatives according to Annex VI of Com- mission Directive 76/768/EEC. This paper describes the preservative effi cacy of the well-known antimicrobial extracts of Lonicera caprifoleum and Lonicera japonica in combination with glyceryl caprylate and/or levulinic acid, p-anisic acid, and ethanol. We prepared a series of acidic (pH=5.5) aqueous and O/W formulations, i.e., tonic lotion, shampoo, shower gel, conditioning cream, anticellulite cream, cleansing milk and peeling cream, con- taining (0.2% w/w) Lonicera extracts, alone in the case of tonic lotion and in combination with (1% w/w) glyc- eryl caprylate in the other products, and we performed challenge tests according to the European Pharmacopoeia procedures and criteria. Formulations such as shampoo, shower gel, and conditioning cream fulfi lled criterion A, while tonic lotion, anticellulite cream, cleansing milk, and peeling cream fulfi lled criterion B, in regard to contamination from A. niger. Furthermore, we evaluated the effi cacy of the antimicrobial systems in two states of use: the intact product and after three weeks of consumer use. The results showed that A. niger was also detected during use by consumers in the products that satisfi ed only criterion B in challenge tests. The addition of antimicrobial fragrance ingredients such (≤ 0.3% w/w) levulinic acid or (0.1% w/w) p-anisic acid and/or (5% w/w) ethanol afforded products that met criterion A in challenge tests and were also microbiologically safe during use. The small quantity (5% w/w) of ethanol gave an important assistance in order to boost the self- preserving system and to produce stable and safe products. INTRODUCTION Microbial spoilage of cosmetic formulations has always been of special concern for industry, since it can lead to product degradation or, in the case of pathogens, constitutes a threat Address all correspondence to A. Varvaresou.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)