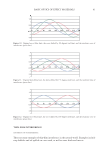
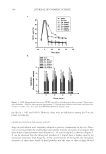
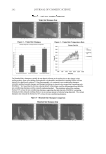
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 150 In the case of the dynamic contact angle measurements, it is necessary to take the scale direction of the hair into account because cuticle cells are attached at the root end and point forward toward the tip end of the hair fi ber. In order to examine the scale direction, a single hair fi ber was cut vertically into two pieces along the line a–b in Figure 1, and the dynamic contact angles were measured by immersing the resulting cut areas in water. Figure 2 shows the typical force curves for untreated hair in the “against scale” (AS) and “with scale” (WS) directions. Figure 3 shows the advancing and receding contact angles for untreated hair in the AS and WS directions. The error bar of each column represents the standard deviation within each group. The asterisk symbol in Figure 3 indicates a signifi cant p-value obtained from Student’s t-test. There was a signifi cant difference in the receding contact angles between the AS and WS directions while there was no signifi cant difference in the advancing contact angles between the AS and WS directions. The reced- ing contact angle for untreated hair was higher in the WS direction than in the AS direction. The results agreed with those of Molina et al. (13) and Kamath et al. (20). Kamath et al. explained their reasons for the receding contact angles for untreated hair being higher in the WS direction than in the AS direction as follows: in the receding mode the frontal edges of the scales provide a lower contact angle (possibly due to scale edge abrasion) in the AS direction, while the dorsal sides of the scales, which are hydrophobic due to the presence of 18-MEA, make a greater contribution in the WS direction, which is Figure 2. Typical contact angle force curves for untreated hair in the “against scale” (AS) and “with scale” (WS) directions. Figure 1. Schematic description of the method for studying the effect of the scale direction of hair on dynamic contact angle measurements.
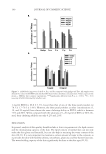
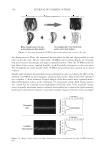
18-MEA AND HAIR APPEARANCE 151 illustrated in Figure 4 (20). Figure 5 shows the schematic description of a hair fi ber, illus- trating the dorsal side versus the frontal side. The frontal side is the edge of the cuticle, which is hydrophilic, most likely, due to removal of 18-MEA by abrasion and scale chip- ping exposing the hydrophilic materials below the epicuticle. The aim of the present study was to identify the roles of 18-MEA on hair appearance, and so the WS direction was chosen for the dynamic contact angle measurements of the hair fi bers. SURFACE PROPERTIES OF HAIR IN A WET ENVIRONMENT Each fi ber was washed with a plain shampoo (15wt% of sodium polyoxyethylene lauryl ether sulfate (2.5 E.O.) with 2wt% N, N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-dodecanamide solution adjusted to pH7 with phosphoric acid) and cut at 5-cm intervals from the root end to the tip. Then, the relative ion yield of 18-MEA versus the CN ion yield on the outermost surface of the hair, dynamic contact angles, and friction force microscopy were measured. Advancing contact angle is the surface property that is related to the water wettability of hair fi bers going from a dry to a wet environment. Receding contact angle is the surface Figure 3. Advancing and receding contact angles for untreated hair in the “against scale” (AS) and “with scale” (WS) directions. The bars represent means for n=5 the whiskers represent the standard deviations. The asterisk symbol indicates the p-value obtained from Student’s t-test *p 0.001. Figure 4. Explanation for the receding contact angles for untreated hair being higher in the WS direction than that in the AS direction. In the receding mode the frontal edges of the scales infl uence a lower contact angle in the AS direction while the dorsal sides of the scales make a greater contribution in the WS direction, as proposed by Kamath et al. (20).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)