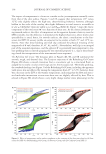
J. Cosmet. Sci., 67, 161–166 (May/June 2016) 161 Development and clinical evaluation of green tea hair tonic for greasy scalp treatment CHANCHANOK NUALSRI, NATTAYA LOURITH, and MAYUREE KANLAYAVATTANAKUL, School of Cosmetic Science, Mae Fah Luang University, Chiang Rai 57100, Thailand. Accepted for publication April 17, 2016. Synopsis Green tea has cosmetic benefi ts that include activities against androgen disorders. A hair tonic containing green tea for reduction of scalp sebum was developed and clinically evaluated. Stable green tea hair tonics were closed-patch tested and clinically evaluated in 20 volunteers for 28 days by using a Sebumeter®. Hair tonic base with glycerin and butylene glycol (total 4%) gained the highest consumers’ preference was incorporated with green tea extract. All of the products were stable and none caused skin irritation. Green tea hair tonic (2%) signifi cantly (p 0.024) lowered scalp sebum for 21 and 28 days following the application, suggesting that this topical therapy of scalp greasiness is safe and effi cient. INTRODUCTION Green tea (Camellia sinensis) has several health benefi ts including favorable cosmetic prop- erties. The herb is therefore widely used in skin care products for antiaging (1,2) and hydration (3,4), either as the single active agent or in a combination with others (5) for skin disorder treatment. Its potential as a hair growth promoter is considered to be caused by 5α-reductase activity (6). In addition, the inhibitory effect of tea against the androgen receptor also implies possible treatments for body and oral malodor (7,8). The clinical setting for hair loss frequently includes oily scalp (6), which is caused by overactive sebaceous glands (9). Excess sebum on the scalp produces the ideal environ- ment for Malassezia spp., resulting in itching and dandruff (10). Therefore, an application of cosmetics to reduce scalp greasiness should be used to manage this hair disorder. In particular, products with a long contact time, such as hair tonics, tend to have enhanced effi cacy (11). Thus, green tea hair tonic was developed and skin irritation was assessed by means of a single closed-patch test including the tonic preference. Thereafter, the devel- oped product was studied and monitored with a Sebumeter® (SM810 CK, Cologne, Germany) in a randomized single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Address all correspondence to Nattaya Lourith at nattayal@mfu.ac.th.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 162 MATERIALS AND METHODS FORMULATIONS AND STABILITY EVALUATION Base hair tonic containing PEG 40-hydrogenated castor oil, menthol, ethyl alcohol, bu- tylene glycol, glycerine (Namsiang, Bangkok, Thailand), and water was formulated as shown in Table I. The pH values of the formulated hair tonics were determined using a PC Testr 35 (Oakton Instruments, Vernon Hills, IL) multifunction analyzer. Three base formulas were tested and found to be stable after an accelerated stability test that was based on a centrifugation assay (3000 rpm for 30 min) in a Micromax RF centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientifi c, Waltham, MA) and six cycles of heating (45°C) and cooling (4°C) for 48 h for each cycle (11). The hair tonic base was incorporated with green tea extract with 100 mg% of polyphenols (product code: HE-EL11-CAS) supplied by Specialty Natural Products (Chonburi, Thailand). The obtained green tea hair tonics were stability tested as above. PREFERENCE TESTS Preference tests for the base hair tonics were carried out with seven female and three male Thai volunteers aged 23–39 years by using a questionnaire with a hedonic scoring system (scores 1–5, where 1 = dislike, 2 = strong preference). The preferred base, which also passed the stability test, was chosen for further hair tonic development (11). CLINICAL EVALUATION Inclusion criteria. Healthy Thai volunteers aged between 23 and 39 years were enrolled in the study. All recruited subjects were informed about the study both in writing and ver- bally, and signed a written consent form that was approved by the ethical committee of the Mae Fah Luang University before enrollment (REH-58062). All of the studies involv- ing human volunteers were in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Table I Formulation, Stability, and Preference of Hair Tonic Base Ingredient Hair tonic base (%, w/w) A B C D E PEG 40-hydrogenated castor oil Menthol Glycerine 4 — 2 4.5 7 Butylene glycol — 4 2 4.5 7 Ethyl alcohol Deionized water Centrifuge Homogeneous Freshly pH 4.10 ± 0.00 4.00 ± 0.00 4.47 ± 0.06 4.40 ± 0.10 4.37 ± 0.12 Heat cool pH 4.47 ± 0.06 4.33 ± 0.06 4.57 ± 0.15 4.47 ± 0.06 4.47 ± 0.06 Overall preference (%) 77.20 ± 6.41 79.60 ± 4.17 84.40 ± 4.79 80.00 ± 5.40 82.20 ± 4.60 91.7 86.7 81.7
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)