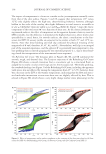
A VALIDATED OMC ANALYSIS: SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHOD 171 monitor their sun protection effi cacies. Obtained UVB absorption effi cacies of 50–87% (13) were based on the presence of OMC as a single UV fi lter, and thereafter all sunscreen products were further analyzed for OMC content. Repeatability of the method. The absorbance values for cosmetic bases used in the SPF deter- minations above were recorded at wavelengths between 200 and 400 nm, with the base- line for each having a smooth pattern and showing no interference over the analytical range. The base was weighted (8 g) for 8 mg/ml OMC that was calculated from 1% OMC in the product. The analytical method is, therefore, specifi c for OMC determination in these prototype sunscreens. The accuracy of OMC levels in these sunscreens was further validated by weighing, conducted on the basis of OMC content at different amounts as described in the Materials and Method section. Recovery values (%) were in the range of 99.76–100.76%, with %RSD being less than 1 as shown in Table IV. Therefore, this analytical method provides an accurate determination of OMC on this basis (11). Inter- estingly, greater recoveries and lower RSD were obtained than in analysis of OMC creams by HPLC (95.6–103.5%, 1.0–2.3% 8), including after extraction using supercritical fl uid (99.55–103.31% 7). Repeatability of the system. OMC sunscreens were subjected to repeat analysis (six times) using the procedure described above. The reproducibility (Table V) was confi rmed by the recovery (%) range (97.23–99.27), and % RSD (0.08–0.50). Table III Accuracy and Precision of OMC Analysis Added amount (μg/ml) Found amount (μg/ml) Absorbance Recovery (%) %RSD The method The system 8.0379 7.8953 0.675 98.23 0.12 0 8.0383 7.9070 0.676 98.37 8.0392 7.9070 0.676 98.36 8.0382 7.9186 0.677 98.51 8.0380 7.9186 0.677 98.51 8.0345 7.9186 0.677 98.56 Table IV Repeatability of the Analytical Method Preparation OMC (%) Recovery ± RSD (%) O/W emulsion 1 99.98 ± 0.06 4 99.76 ± 0.08 7.5 100.04 ± 0.23 W/O emulsion 1 100.02 ± 0.12 4 100.76 ± 0.02 7.5 99.98 ± 0.09 Mineral oil 1 100.04 ± 0.28 4 99.93 ± 0.10 7.5 100.04 ± 0.10
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 172 CONCLUSIONS Determination of OMC in sunscreens was achieved using a UV-spectrophotometric method validated according to ICH and AOAC guidelines (11,12). Methanol was found to be the optimal solvent, with the method showing an analytical linearity range between 4 and 12 μg/ml with a determination coeffi cient of 0.999. Furthermore, the method was applicable to emulsions containing 1%, 4%, and 7.5% of OMC, including those in min- eral oil. Thus, this method is an inexpensive, simple, rapid, accurate, and precise way to determine the OMC content in sunscreen products (5), and could be a viable alternative to HPLC and MECC methods (2,5,7,8). However, this validated method is only suitable for sunscreen products comprising solely OMC as the UV fi lter, without some type of chromatographic separation, any other chemical species with an absorbance in the range of OMC could cause interference and might lead to erroneous results. The challenge is to expand the scope of this method for the detection of different suncare actives and for use in other formulations to enhance its potential quality assurance applications in the phar- maceutical industry. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Mae Fah Luang University is acknowledged for facilities support and the manuscript preparation. REFERENCES (1) E. Gilbert, F. Pirot, V. Bertholle, L. Roussel, F. Falson, and K. Padois, Commonly used UV fi lter toxic- ity on biological functions: Review of last decade studies, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 35, 208–209 (2013). (2) P. Kullavanijaya and H. W. Lim, Photoprotection, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 52, 937–958 (2005). (3) K. Jung, M. Seifert, Th. Herrling, and J. Fuchs, UV-generated free radicals (FR) in skin: Their preven- tion by sunscreens and their induction by self-tanning agents, Spectrochim. Acta A., 69, 1423–1428 (2008). (4) A. O. Barel, M. Pay, and H. I. Maibach, Handbook of Cosmetic Science and Technology, 3rd Ed. (Informa Healthcare, New York, NY, 2009). (5) J. Cheng, Y.-L. Li, R. L. Roberts, and G. Walker, Analysis of 2-ethylhexyl-p methoxycinnamate in sun- screen products by HPLC and Raman spectroscopy, Talanta, 44, 1807–1813 (1997). (6) Y. Shih and F.-C. Cheng, Determination of sunscreen agents in cosmetic products using microwave- assisted extraction and liquid chromatography, J. Chromatogr. A., 876, 243–246 (2000). Table V Repeatability of the Analytical System Preparation OMC (%) SPF Recovery ± RSD (%) O/W emulsion 1 2.83 ± 0.11 96.08 ± 0.14 4 5.12 ± 0.79 98.50 ± 0.08 7.5 8.27 ± 0.59 97.23 ± 0.29 W/O emulsion 1 2.18 ± 0.43 99.06 ± 0.10 4 6.30 ± 0.48 97.56 ± 0.16 7.5 8.28 ± 0.90 99.11 ± 0.17 Mineral oil 1 2.50 ± 0.22 98.25 ± 0.50 4 6.29 ± 0.62 98.01 ± 0.10 7.5 8.65 ± 0.76 99.27 ± 0.19
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)