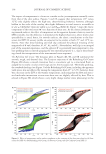
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 188 D-SQUAME ANALYSIS SCHEME The protein content of all D-Squame sampling discs was analyzed nondestructively by measuring the optical absorption with a SquameScan™ 850A infrared densitometer (Heiland Electronic, Wetzlar, Germany). The device measures optical absorption at 850 nm, which is linearly related to protein content of the D-Squame sample (25). SC cyto- kines (IL-1α and IL-1ra) were measured using tape 2, and NMF components were mea- sured using tape 3 and tape 10. Structural proteins (involucrin, keratin-1,10,11) were measured on tape 4, and SC lipids were measured using tapes 6 and 7 pooled together for better sensitivity. Measurements for cytokines, NMF, and structural proteins were nor- malized to protein measured by the Pierce® BCA protein assay (Thermo Scientifi c, Rockford, IL) and lipids were normalized to SquameScan™ values. Analysis of NMFs from D-Squame discs. NMF samples (L-citrulline, glycine, L -ornithine, L -pro- line, 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic acid, L -serine, t-UA, and L -histidine) collected on D-Squame discs were prepared for analysis by placing the discs into 2-ml polypropylene tubes with the glue side facing inward. A 25-μl aliquot of an internal standard solution (L-citrulline-D7 glycine-D2,15N histidine-D3 L -ornithine-D6 L -proline-D3 2-pyrrolidone-5-carboxylic-D5 acid L -serine-D3 cis-urocanic-13C3 acid) was added to each tube followed by 1.0 ml of water containing 0.1% formic acid and 0.1% heptafl uorobutyric acid. The tubes were capped, vor- texed for 10 s and then placed on a sonicator for 10 min. An aliquot of the extraction solution was removed for analysis by gradient reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis on a Waters Atlantis T3 (Milford, MA) column (2.1 x 50 mm, 3-μm particles). De- tection and quantitation was performed using tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS Sciex AB- 5000) operating under multiple reaction monitoring conditions for each analyte and the corresponding internal standard. Calibration standards prepared in 1.0 ml of water containing 0.1% formic acid and 0.1% heptafl uorobutyric acid were used to generate regression curves for each NMF by plotting the peak area ratio for a given NMF standard (peak area NMF/peak area for internal standard) versus the standard concentration. The concentration of a given NMF in the study samples was determined from its corresponding peak area ratio by interpo- lation from the regression curve. The nominal range of quantitation is 20–20,000 ng/ml (20–20,000 ng/tape strip) for each NMF. The concentration of each NMF determined in the acid extract was converted into mass NMF/strip by multiplying by the extraction volume. The calculated mass of each NMF was then normalized by the protein amount in the acid extract determined by BCA assay using bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Analysis of IL-1α and IL-1ra from D-Squame discs. Human infl ammatory cytokines were analyzed to evaluate skin irritation and infl ammatory processes. D-Squame discs collected from subjects were extracted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing an addi- tional 0.25 M NaCl and a commercially available protease inhibitor cocktail containing a mixture of protease inhibitors with broad-spectrum inhibitory specifi city (Roche Applied Science, Inc., Indianapolis, IN) for 30 min with sonication on ice. The extracts were then centrifuged for 5 min at 2100 × g to remove skin solids that might interfere in the assay. Aliquots of these extracts were then analyzed for soluble protein using the BCA Protein Assay Kit and BSA as a reference standard. After protein analysis, extracts were supple- mented with 2% BSA, transferred into 96-well polypropylene deep-well plates and fro- zen at -80°C for cytokine analysis. Multiple human cytokines (IL-1α and IL-1ra) were simultaneously quantitated using a Milliplex Human Cytokine Multiplex Immunoassay Kit (Millipore Corp., Billerica, MA).
EFFECTS OF SEASON ON STRATUM CORNEUM 189 Analysis of skin proteins from D-Squame discs. D-Squame discs were extracted with PBS containing 0.2% sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.5% propylene glycol for 30 min with sonication on ice. The extracts were then centrifuged for 5 min at 2100 × g to remove skin solids that might interfere in the assay. Subsequently, the extracts of D-Squame discs were transferred into 96-well polypropylene deep-well plates and frozen at -80°C for skin multiple analyte profi le (SkinMAP) and soluble protein analyses. Human skin proteins (keratin-1,10, involucrin, human serum albumin) were simultaneously quantifi ed using a 3-plex Human Skin Panel Multiplex Immunoassay Kit (Millipore Corp.). The antibody for human involucrin recognizes non-cross-linked involucrin protein, but may have reac- tivity with involucrin within the cornifi ed envelope. Soluble protein was measured using BCA Protein Assay Kit. Analysis of skin lipids from D-Squame discs. An array of skin lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol sulfate, selected fatty acids, and selected ceramides—see Table III for ceramide nomencla- ture) was determined from extracts of D-Squame discs containing samples from human skin using gradient supercritical fl uid chromatography (SFC) with MS/MS with detection in the positive and negative ionization modes depending on the analyte using atmo- spheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI). The tape strips were fi rst analyzed via a SquameScan™ 850A infrared densitometer to determine the amount of removed skin for normalization of the measured lipids. Two tape strips from each subject were transferred to 20-ml glass vials, spiked with an internal standard mixture [D6-cholesterol, D7-cho- lesterol sulfate, D47-tetradecanoic acid, D3-heptadecanoic acid, D7-sphinanine, and D31- N-palmitoyl-1-D-erythro-sphingosine (D31-Ceramide)] and extracted using 3 ml of methanol followed by sonication at ambient temperature. The vials were centrifuged, and the methanol layer removed and placed in separate glass vial. The tape strips were then extracted with 3 ml of hexane followed by sonication for 15 min at ambient temperature, and the hexane layer was separated. The hexane and methanol layers for each set of tapes were then combined, dried under nitrogen at 50°C, and fi nally reconstituted in chloroform:MeOH (3:1 v/v). Standards [myristic acid, palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, octadecanoic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, docosanoic acid, tetracosanoic acid, choles- terol, cholesterol sulfate, N(24_0)P(18), N(24_0)DS(18), A(16_0)S(18), A(24_0)P(18), ceramide EOS-C30, S(18)] were prepared in chloroform:MeOH (3:1) over a range of ap- propriate concentrations. The standards, spiked with internal standard, and the reconsti- tuted samples were analyzed by gradient SFC with MS/MS detection using APCI. The fatty acids were monitored in the negative ion mode while selected ceramides, sphingoid bases, cholesterol, and cholesterol sulfate were monitored in the positive ion mode. The peak area ratio (standard peak area/internal standard peak area) for each standard level were used to construct a linear regression curve for each of the standard analytes. For ana- lytes, where the standard was available (fatty acids, cholesterol, cholesterol sulfate, sphin- goid bases), the actual standard was used, whereas for the ceramides the surrogate ceramide for the particular class was used. The lipid mass found for each analyte was divided by the SquameScan values for the corresponding tapes. STATISTICAL METHODS: SKINMAP, NMF, CYTOKINES, AND LIPIDS For each of the four sites within a subject, the SkinMAP (tape 4), NMF (tapes 3 and 10), cytokines (tape 2), and lipids (tape 6 and 7 pooled) measures were normalized to their associated protein measures (BCA for SkinMAP, NMF, and cytokines and SquameScan™
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)