214 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS As part of a program to develop methods for detecting NDELA in cosmetics and related matrices, we have refined and validated the HPLC-TEA analytical method. This paper presents the results of this work. EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS The isocratic HPLC system consisted of a Waters Associates (Milford, Mass.) Model 6000A pump, Waters Model U6K injector, Carle Instruments (Anaheim, Calif.) Model 2025 four-way micro-switching valve, Waters Model 440 UV detector operated at 254 nm, and a Thermo Electron Corporation (Waltham, Mass.) TEA Model 502. The UV and TEA detectors were used in series, the UV used first. The TEA was operated at a furnace temperature of 550øC, argon and oxygen pressures were 0.5 torr, photomul- tiplier voltage was 1475 V DC, and the cold trap was dry ice/isopropanol. The columns were Waters txBondapak CN (300 X 4 mm ID) a Laboratory Data Control (Riviera Beach, Fla.) 5 txm Spherisorb CN (250 x 4.6 mm ID) with a Whatman (Clifton, N.Y.) Co:Pell octadecyl silane guard column and a Laboratory Data Control 5 txm Spherisorb Silica (250 X 4.6 mm ID) with a Co:Pell silica guard column. Unless otherwise specified, flow rates were 2 mL/min isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol (75/19/6 volumetric ratios are used throughout this report). The micro-switching valve was placed in the system between the UV detector and the TEA detector to permit the analyst to switch the column eluent from the TEA detector to waste when desired, based upon the UV response. REAGENTS All solvents were HPLC "distilled in glass" grade (Burdick and Jackson, Muskegon, Mich.) and filtered prior to use in the HPLC system. Reagent-grade compounds used as chromatographic standards were obtained from other research projects at Midwest Research Institute. PROCEDURE Calibration of the HPLC-TEA system. Reference solutions of NDELA in the same solvent system as used for preparing samples were employed to evaluate the linearity of the TEA response to NDELA and to determine the stability of the HPLC-TEA system. A minimum of three reference solution concentrations of NDELA, e.g., 20, 50, and 100 ng/ml, were prepared with each sample set. Each of these solutions was analyzed prior to determining NDELA in a sample set, and a reference solution was analyzed prior to each sample. The relative weight response (RWR) for the reference solution was determined from the measured peak heights (PH) and known weights (wt) of NDELA and the N-nitrosopyrrolidine (NPYR) internal chromatographic standard by: PH NDELA wt NPYR RWR = X PH NPYR wt NDELA The RWR factor was determined for each reference solution analyzed during a sample set. If the RWR factor varied more than 10% from that of the previous solution, sample analysis was terminated until the proper response factor could again be obtained.
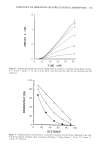
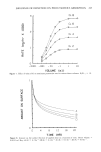
HPLC-TEA ANALYSIS OF NDELA 215 The average response factor was employed to determine the level of NDELA present in each of the samples analyzed. Sample analysis. As discussed below, the final procedure was as follows: 1. Quantitatively add -5 ng/injection (e.g., 100 •tL of 500 ng/mL) of NPYR in chromatographic solvent and dilute the sample to a known volume (e.g., 5 ml). 2. Inject a known volume (50-75 •1) of each sample onto a Spherisorb CN column (Laboratory Data Control) with a Series B- 110, 0 to 100 •1 syringe (Applied Science Laboratory, State College, Penn.). 3. Monitor the UV response at 0.1 to 0.5 absorbance units full scale and the TEA response at an attenuation of X 2. 4. Before each sample injection analyze a reference solution of NDELA to ensure reproducible TEA response. When possible, select a reference solution which cor- responds to the estimated level of NDELA in the next sample. Method of calculation. The level of NDELA in a sample was calculated from the TEA peak height (PH) response to NDELA in the sample and in reference solutions by the following simple rearrangement of the RWR equation, PH NDELA wt NPYR wt NDELA/aliquot = X PH NPYR RWR Table I HPLC Parameter Evaluation for NDELA Determination (Spherisorb Silica, 5 •m) Flow NDELA a Eluent Rate k' PAF b W0.1 c (min) 50/45/5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/45/5 Hexane/methylene chloride/methanol 75/22.5/2.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/49/1 Isopropanol/hexane/methanol 75/24.5/0.5 Isopropanol/hexane/methanol 75/25 Isopropanol/isooctane 50/50 Isopropanol/isooctane 73.5/25/1.5 Methylene chloride/isopropanol/ acetonitrile 75/25 Methylene chloride/isopropanol 50/50 Hexane/isopropanol 80/16/4 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 65/31.5/3.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 50/47.5/2.5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 65/33.25/1.75 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 75/20/5 Isooctane/isopropanol/methanol 60/30/10 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 75/19/6 Isooctane/methylene chloride/methanol 3.0 0.9 1.2 0.5 2.0 •0 1.3 1.4 3.0 1.7 3.5 1.1 2.0 1.0 4.3 1.5 2.0 1.0 2.5 1.1 2.0 1.0 4.5 1.3 2.0 •0 5.0 1.9 2.0 •0 4.4 1.7 2.0 --0 4.3 1.5 2.0 •0 5.7 3.9 1.0 2.3 1.3 1.2 1.0 1.0 3.0 1.7 1.0 0.9 1.8 1.2 2.0 1.1 1.7 0.7 1.0 1.3 1.8 1.1 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.6 1.0 2.0 1.6 1.0 1.5 1.5 0.6 0.5 1.5 3.3 0.7 0.7 elution volume NDELA--void volume a k' = void volume width of back half of peak at 10% height b PAF = peak asymmetry factor = width of front half of peak at 10% height c W0 • = width of peak at 10% height.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)